A
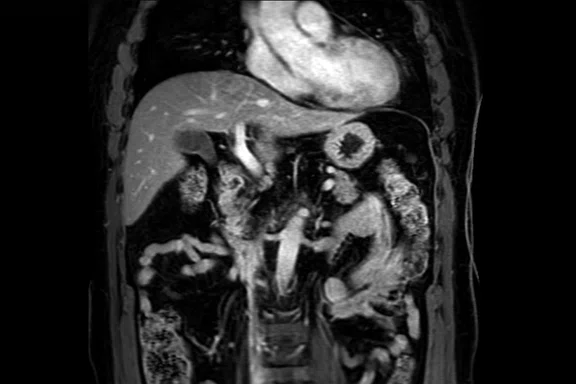
Figure 1.
A fully navigated pediatric abdomen exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Axial T2w FatSat; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial DWI b800; (D) axial LAVA Flex, water only; (E) coronal T2w FatSat SSFSE; (F) coronal LAVA Flex, water only; and (G) coronal LAVA Flex in-phase.
B
Figure 1.
A fully navigated pediatric abdomen exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Axial T2w FatSat; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial DWI b800; (D) axial LAVA Flex, water only; (E) coronal T2w FatSat SSFSE; (F) coronal LAVA Flex, water only; and (G) coronal LAVA Flex in-phase.
C
Figure 1.
A fully navigated pediatric abdomen exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Axial T2w FatSat; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial DWI b800; (D) axial LAVA Flex, water only; (E) coronal T2w FatSat SSFSE; (F) coronal LAVA Flex, water only; and (G) coronal LAVA Flex in-phase.
D
Figure 1.
A fully navigated pediatric abdomen exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Axial T2w FatSat; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial DWI b800; (D) axial LAVA Flex, water only; (E) coronal T2w FatSat SSFSE; (F) coronal LAVA Flex, water only; and (G) coronal LAVA Flex in-phase.
A
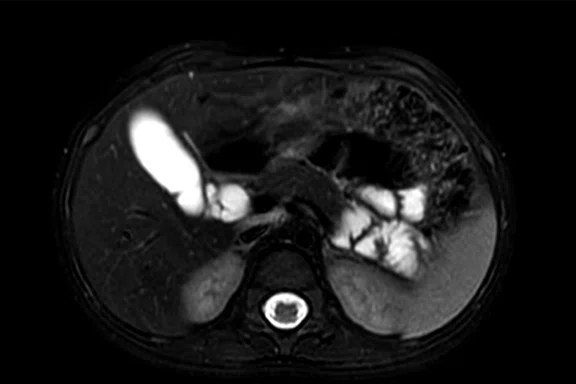
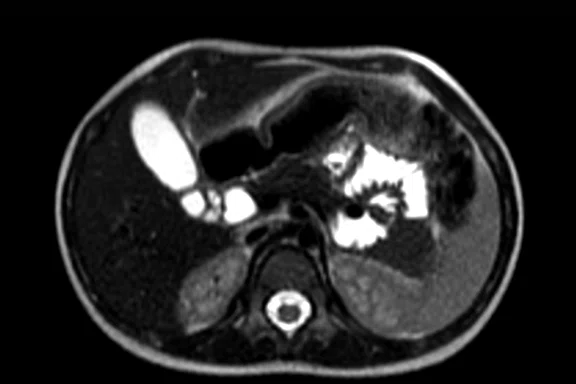
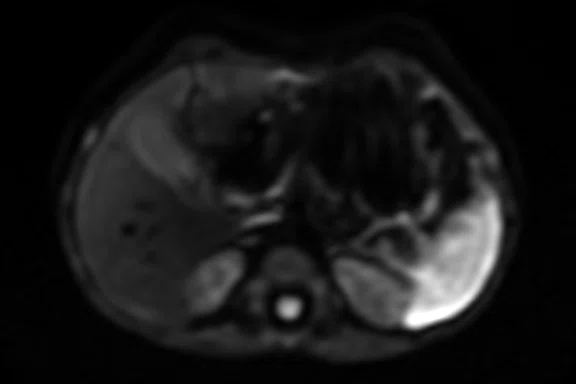
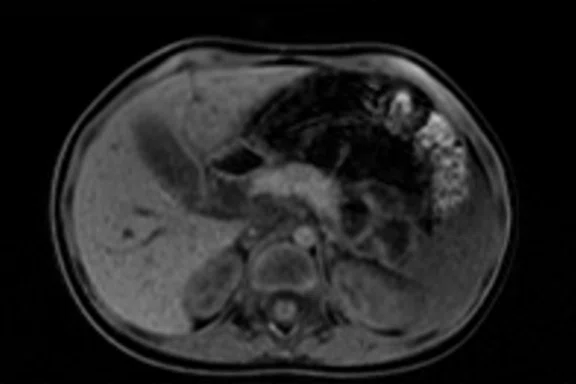
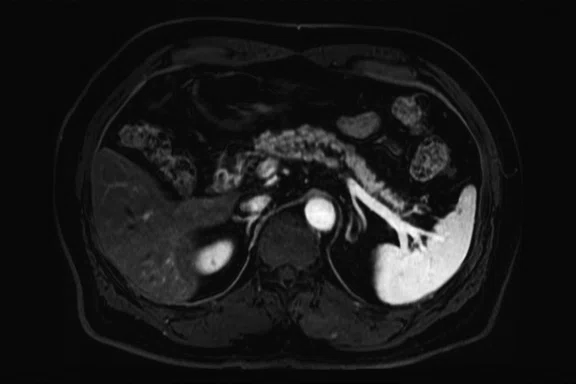
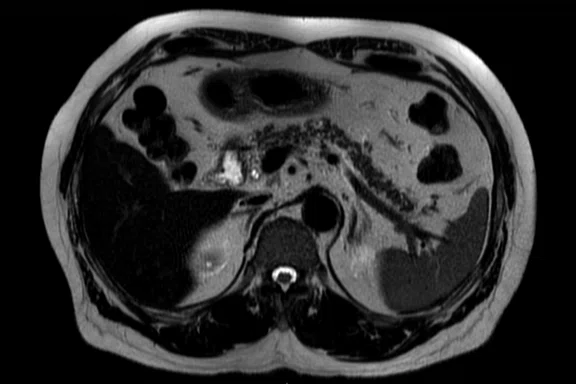
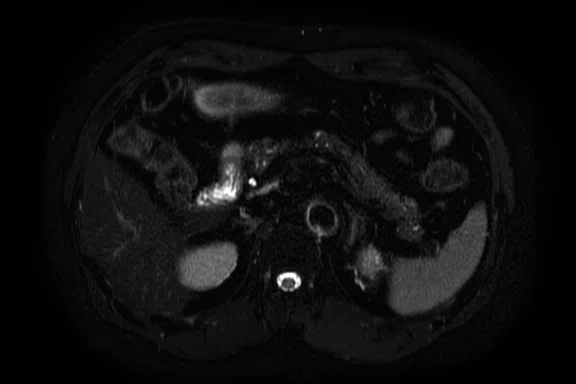
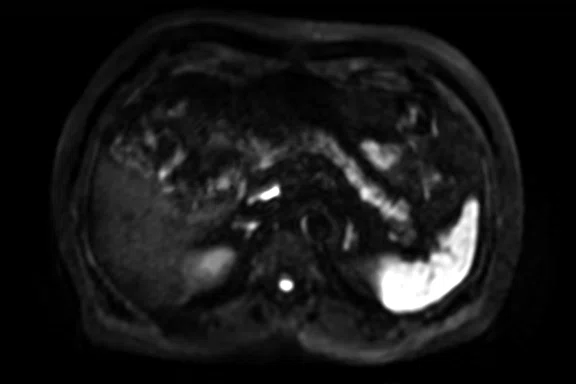
Figure 2.
Pancreas exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Dynamic LAVA Flex, 1.1 x 1.8 x 1.4 mm, 20 sec., 3 phases; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial T2w FatSat; (D) axial DWI b800; and (E) contrast-enhanced coronal LAVA Flex.
B
Figure 2.
Pancreas exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Dynamic LAVA Flex, 1.1 x 1.8 x 1.4 mm, 20 sec., 3 phases; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial T2w FatSat; (D) axial DWI b800; and (E) contrast-enhanced coronal LAVA Flex.
C
Figure 2.
Pancreas exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Dynamic LAVA Flex, 1.1 x 1.8 x 1.4 mm, 20 sec., 3 phases; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial T2w FatSat; (D) axial DWI b800; and (E) contrast-enhanced coronal LAVA Flex.
D
Figure 2.
Pancreas exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Dynamic LAVA Flex, 1.1 x 1.8 x 1.4 mm, 20 sec., 3 phases; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial T2w FatSat; (D) axial DWI b800; and (E) contrast-enhanced coronal LAVA Flex.
E
Figure 2.
Pancreas exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Dynamic LAVA Flex, 1.1 x 1.8 x 1.4 mm, 20 sec., 3 phases; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial T2w FatSat; (D) axial DWI b800; and (E) contrast-enhanced coronal LAVA Flex.
A
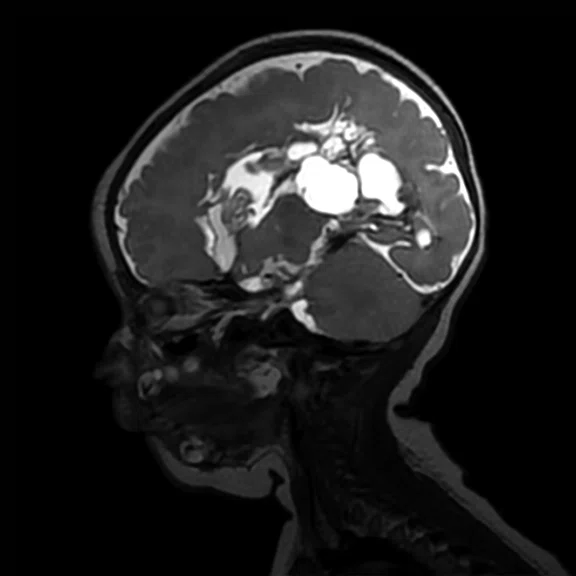
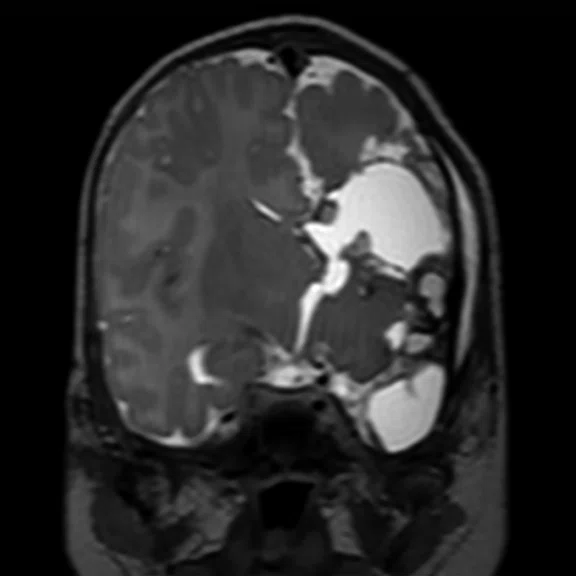
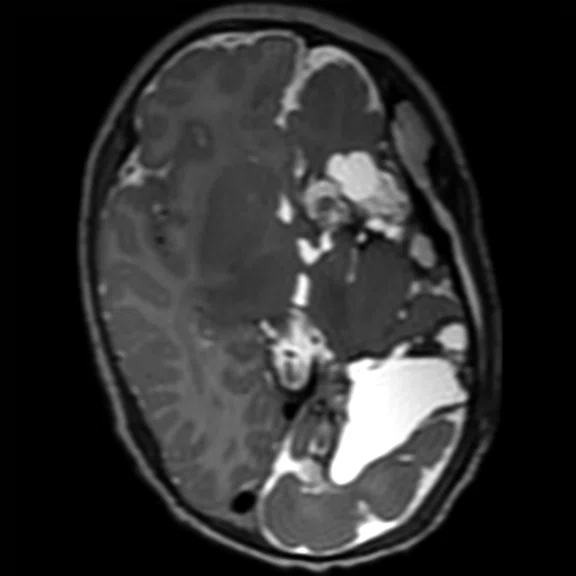
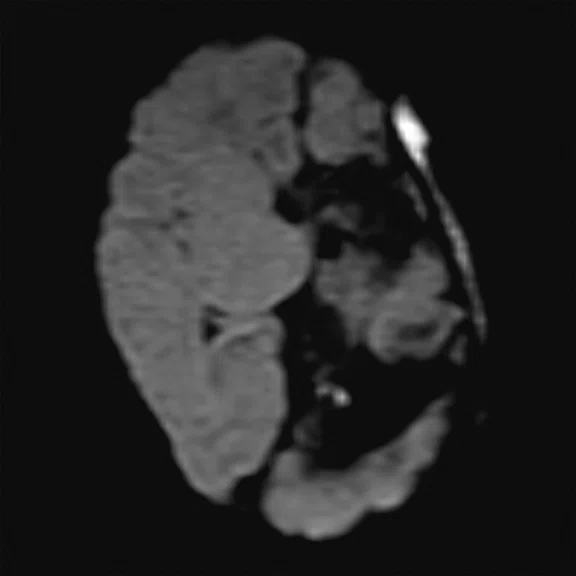
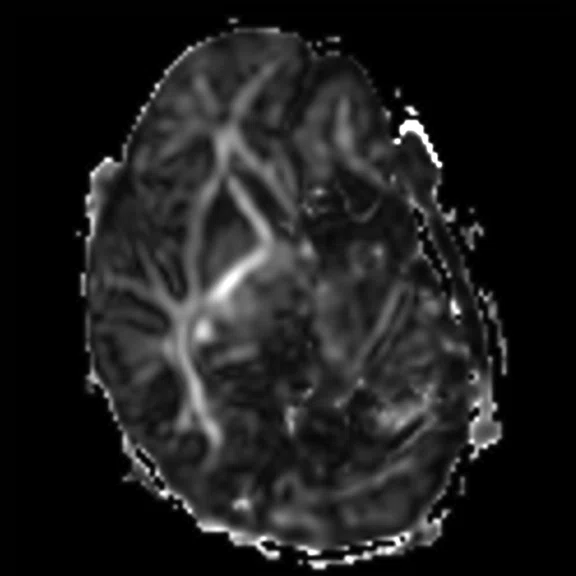
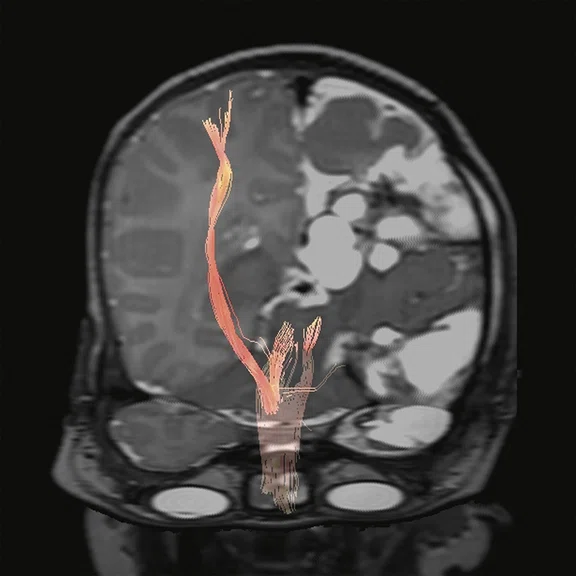
Figure 4.
Pediatric brain study. (A) Sagittal T2w Cube, 0.9 x 0.9 x 1.2 mm, 3:04 min. with (B) coronal MPR and (C) axial MPR; (D) axial DWI b1000 with HyperBand; (E) DTI with HyperBand 25 direction FA map; and (F) DTI 25 direction tractography.
B
Figure 4.
Pediatric brain study. (A) Sagittal T2w Cube, 0.9 x 0.9 x 1.2 mm, 3:04 min. with (B) coronal MPR and (C) axial MPR; (D) axial DWI b1000 with HyperBand; (E) DTI with HyperBand 25 direction FA map; and (F) DTI 25 direction tractography.
C
Figure 4.
Pediatric brain study. (A) Sagittal T2w Cube, 0.9 x 0.9 x 1.2 mm, 3:04 min. with (B) coronal MPR and (C) axial MPR; (D) axial DWI b1000 with HyperBand; (E) DTI with HyperBand 25 direction FA map; and (F) DTI 25 direction tractography.
D
Figure 4.
Pediatric brain study. (A) Sagittal T2w Cube, 0.9 x 0.9 x 1.2 mm, 3:04 min. with (B) coronal MPR and (C) axial MPR; (D) axial DWI b1000 with HyperBand; (E) DTI with HyperBand 25 direction FA map; and (F) DTI 25 direction tractography.
E
Figure 4.
Pediatric brain study. (A) Sagittal T2w Cube, 0.9 x 0.9 x 1.2 mm, 3:04 min. with (B) coronal MPR and (C) axial MPR; (D) axial DWI b1000 with HyperBand; (E) DTI with HyperBand 25 direction FA map; and (F) DTI 25 direction tractography.
F
Figure 4.
Pediatric brain study. (A) Sagittal T2w Cube, 0.9 x 0.9 x 1.2 mm, 3:04 min. with (B) coronal MPR and (C) axial MPR; (D) axial DWI b1000 with HyperBand; (E) DTI with HyperBand 25 direction FA map; and (F) DTI 25 direction tractography.
A
Figure 5.
Pelvis exam with AIR™ Recon using Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and NEX 1.5 to reduce scan times. (A) Axial T2w FatSat with PROPELLER MB, FOV 30 cm, 1:44 min. and (B) sagittal T2w FatSat with PROPELLER MB, FOV 30 cm, 2:18 min.
B
Figure 5.
Pelvis exam with AIR™ Recon using Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and NEX 1.5 to reduce scan times. (A) Axial T2w FatSat with PROPELLER MB, FOV 30 cm, 1:44 min. and (B) sagittal T2w FatSat with PROPELLER MB, FOV 30 cm, 2:18 min.
E
Figure 1.
A fully navigated pediatric abdomen exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Axial T2w FatSat; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial DWI b800; (D) axial LAVA Flex, water only; (E) coronal T2w FatSat SSFSE; (F) coronal LAVA Flex, water only; and (G) coronal LAVA Flex in-phase.
F
Figure 1.
A fully navigated pediatric abdomen exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Axial T2w FatSat; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial DWI b800; (D) axial LAVA Flex, water only; (E) coronal T2w FatSat SSFSE; (F) coronal LAVA Flex, water only; and (G) coronal LAVA Flex in-phase.
G
Figure 1.
A fully navigated pediatric abdomen exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil. (A) Axial T2w FatSat; (B) axial T2w SSFSE; (C) axial DWI b800; (D) axial LAVA Flex, water only; (E) coronal T2w FatSat SSFSE; (F) coronal LAVA Flex, water only; and (G) coronal LAVA Flex in-phase.
A
Figure 3.
The wide coverage and good uniformity provided by the AIR™ AA Coil enables both upper arms to be acquired in one scan. (A) Coronal STIR, 1.0 x 1.4 x 4.0 mm, 3:25 min.; (B) axial STIR, 1.0 x 1.5 x 4 mm, 2:32 min.; and (C) axial T1w, 0.8 x 1.3 x 5 mm, 2:25 min.
B
Figure 3.
The wide coverage and good uniformity provided by the AIR™ AA Coil enables both upper arms to be acquired in one scan. (A) Coronal STIR, 1.0 x 1.4 x 4.0 mm, 3:25 min.; (B) axial STIR, 1.0 x 1.5 x 4 mm, 2:32 min.; and (C) axial T1w, 0.8 x 1.3 x 5 mm, 2:25 min.
C
Figure 3.
The wide coverage and good uniformity provided by the AIR™ AA Coil enables both upper arms to be acquired in one scan. (A) Coronal STIR, 1.0 x 1.4 x 4.0 mm, 3:25 min.; (B) axial STIR, 1.0 x 1.5 x 4 mm, 2:32 min.; and (C) axial T1w, 0.8 x 1.3 x 5 mm, 2:25 min.
A
Figure 6.
Elbow exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil, Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and AIR™ Recon. (A) Coronal T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (B) coronal T1w, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (C) axial T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:41 min.; and (D) axial contrast-enhanced T1w Flex, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 2:09 min.
B
Figure 6.
Elbow exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil, Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and AIR™ Recon. (A) Coronal T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (B) coronal T1w, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (C) axial T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:41 min.; and (D) axial contrast-enhanced T1w Flex, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 2:09 min.
C
Figure 6.
Elbow exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil, Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and AIR™ Recon. (A) Coronal T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (B) coronal T1w, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (C) axial T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:41 min.; and (D) axial contrast-enhanced T1w Flex, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 2:09 min.
D
Figure 6.
Elbow exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil, Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and AIR™ Recon. (A) Coronal T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (B) coronal T1w, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (C) axial T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:41 min.; and (D) axial contrast-enhanced T1w Flex, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 2:09 min.
A
Figure 3.
The wide coverage and good uniformity provided by the AIR™ AA Coil enables both upper arms to be acquired in one scan. (A) Coronal STIR, 1.0 x 1.4 x 4.0 mm, 3:25 min.; (B) axial STIR, 1.0 x 1.5 x 4 mm, 2:32 min.; and (C) axial T1w, 0.8 x 1.3 x 5 mm, 2:25 min.
B
Figure 3.
The wide coverage and good uniformity provided by the AIR™ AA Coil enables both upper arms to be acquired in one scan. (A) Coronal STIR, 1.0 x 1.4 x 4.0 mm, 3:25 min.; (B) axial STIR, 1.0 x 1.5 x 4 mm, 2:32 min.; and (C) axial T1w, 0.8 x 1.3 x 5 mm, 2:25 min.
C
Figure 3.
The wide coverage and good uniformity provided by the AIR™ AA Coil enables both upper arms to be acquired in one scan. (A) Coronal STIR, 1.0 x 1.4 x 4.0 mm, 3:25 min.; (B) axial STIR, 1.0 x 1.5 x 4 mm, 2:32 min.; and (C) axial T1w, 0.8 x 1.3 x 5 mm, 2:25 min.
A
Figure 6.
Elbow exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil, Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and AIR™ Recon. (A) Coronal T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (B) coronal T1w, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (C) axial T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:41 min.; and (D) axial contrast-enhanced T1w Flex, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 2:09 min.
B
Figure 6.
Elbow exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil, Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and AIR™ Recon. (A) Coronal T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (B) coronal T1w, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (C) axial T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:41 min.; and (D) axial contrast-enhanced T1w Flex, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 2:09 min.
C
Figure 6.
Elbow exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil, Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and AIR™ Recon. (A) Coronal T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (B) coronal T1w, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (C) axial T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:41 min.; and (D) axial contrast-enhanced T1w Flex, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 2:09 min.
D
Figure 6.
Elbow exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil, Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and AIR™ Recon. (A) Coronal T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (B) coronal T1w, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (C) axial T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:41 min.; and (D) axial contrast-enhanced T1w Flex, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 2:09 min.
result


PREVIOUS
${prev-page}
NEXT
${next-page}
Subscribe Now
Manage Subscription
FOLLOW US
Contact Us • Cookie Preferences • Privacy Policy • California Privacy PolicyDo Not Sell or Share My Personal Information • Terms & Conditions • Security
© 2024 GE HealthCare. GE is a trademark of General Electric Company. Used under trademark license.
IN PRACTICE
AIR breathes new life into MR imaging excellence
AIR breathes new life into MR imaging excellence
After implementing AIR™ technologies – the AIR™ Anterior Array (AA) Coil, AIR™ Recon and AIR x™ – Seirei Hamamatsu has achieved improvements in workflow, image quality and the patient experience. The new technologies have also impacted clinical confidence due to greater scan consistency, fewer artifacts, and improved SNR and image uniformity.
After implementing AIR™ technologies – the AIR™ Anterior Array (AA) Coil, AIR™ Recon and AIR x™ – Seirei Hamamatsu has achieved improvements in workflow, image quality and the patient experience. The new technologies have also impacted clinical confidence due to greater scan consistency, fewer artifacts, and improved SNR and image uniformity.
Takayuki Masui, MD, PhD, Hospital Assistant Director, Director of the Health Information Center and Chief of the Department of Radiology at Seirei Hamamatsu General Hospital in Hamamatsu, a coastal city in Honshu, Japan’s main island, is seeing imaging improvements across the board with several AIR™ technologies.
The hospital recently implemented AIR™ Coils, the industry’s first suite of RF coils that enable greater positioning freedom during an MR scan. According to Dr. Masui, patients used to complain about the weight of traditional coils every week, but those complaints stopped when AIR™ Coils were introduced.
AIR™ Coils are up to 60 percent lighter than conventional coils, benefiting both patients and technologists. The coils offer greater flexibility to help conform to patients’ anatomies and fit all patient ages, sizes and shapes. Additionally, AIR™ Coils enable increased acceleration factors in parallel imaging due to high coil density. AIR™ Coils were recently named Best New Radiology Device by AuntMinnie.com in the 2019 Minnies Competition.
Seirei Hamamatsu has five GE Healthcare MR systems, including the SIGNA™ Pioneer with AIR™. "If the techs could choose an MR system, they would choose the SIGNA™ Pioneer because it can be used with the AIR™ Coils," said Dr. Masui.
The AIR™ AA Coil is designed to conform to the human body. The ultra-lightweight design makes it easier to scan the patient and addresses several clinical needs, including large field-of-view coverage when scanning chest, abdomen and pelvis exams without repositioning the patient or the coil.
Previously, clinicians at Seirei Hamamatsu had challenges when using GE’s Phased-array Uniformity Enhancement (PURE) with a conventional 16-channel AA coil due to noise near a central area, such as the pancreas. The AIR™ AA Coil improved SNR and uniformity, enabling them to use PURE.
AIR™ Coils are also improving workflow. "With conventional coils, it was difficult to change the setting during the examination, but now those changes can be easily performed with the AIR™ Coil," he says. "Furthermore, the coil can flexibly respond to changes in a patient’s positioning during the exam."
The facility is also using AIR Touch™, an automated workflow solution, to help improve scan productivity and usability, and potentially help facilitate shorter scan times. "AIR Touch™ is very convenient because it automatically selects the coil elements."
Improved productivity with AIR x™
Seirei Hamamatsu has also implemented AIR x™, a deep-learning-based, intelligent workflow solution for brain scanning that increases consistency and productivity in their clinical practice.
"AIR x™ automatically finds the midline in sagittal scans and adjusts the incline in axial scans, which has helped us reduce the total brain exam time anywhere from 30 seconds to 1 minute."
Dr. Takayuki Masui
AIR x™ provides automated slice prescriptions to help reduce previously redundant, manual steps. It produces images that have less variability between technologists and between scans, to lower the chances for a patient to be recalled due to incorrect slice placement. And regardless of how the patient’s head is positioned, AIR x™ selects the right slice position. An increase in consistency is particularly important when doing longitudinal assessments for diseases like Alzheimer’s and multiple sclerosis.
Technologists can set up exams five times faster and perform four times fewer mouse clicks using AIR x™. This new tool features a pre-trained neural network model that leverages deep-learning algorithms with anatomy recognition to define the correct anatomical landmarks and automates the scanning process for routine to challenging set-ups. The algorithm automatically aligns the prescribed slices to anatomical references that are trained on a database of over 36,000 images sourced from clinical studies and reference sites.
AIR x™ has helped increase clinical confidence and accuracy in patient management as a result of the consistent slice prescriptions between MR studies taken at different times.
"In brain MR angiography scans (TOF), the scanning plane can be set with high accuracy for the Circle of Willis," Dr. Masui says. "Accuracy for the pituitary gland and a sagittal view of the optic nerve is also good."
In fact, during an orbital tumor case, he encountered an optic nerve that was curved due to the tumor, which was visible thanks to the precise slice prescription made possible with AIR x™.
"I think study times will continue to improve, especially in the case of older patients with slower blood flow from atherosclerosis, where slab settings may affect the degree of visualization of the vessels in a multislab brain MRA study due to differences in inflow effects between slabs. The same slab setting with AIR x™ may help reduce the total patient exam time while maintaining the reproducible visualization of the vessels across repeat exams," Dr. Masui adds.
AIR™ Recon for clear images and fast scans
AIR™ Recon, a new reconstruction technique available in the SIGNA™Works AIR™ Edition software release, is making exceptional image quality in shorter scan times, which is the new standard for excellence in MR imaging.
After the software upgrade, AIR™ Recon immediately helped the facility reduce wrap-around artifacts, which shortened scanning time by decreasing the oversampling factor. "In the female pelvis, AIR™ Recon reduced scanning time anywhere from about 1 to 1:30 minutes. In the spine, we have the same benefits, so we expect to see high throughput in these exams as well."
Figure 6.
Elbow exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil, Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and AIR™ Recon. (A) Coronal T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (B) coronal T1w, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (C) axial T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:41 min.; and (D) axial contrast-enhanced T1w Flex, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 2:09 min.
Figure 6.
Elbow exam with the 30ch AIR™ AA Coil, Flexible No Phase Wrap 1.5 and AIR™ Recon. (A) Coronal T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (B) coronal T1w, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:33 min.; (C) axial T2w FatSat, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 1:41 min.; and (D) axial contrast-enhanced T1w Flex, 0.4 x 0.5 x 3 mm, 2:09 min.
AIR™ Recon has also helped reduce background noise and artifacts. "With the implementation of AIR™ Recon, the streak artifacts from PROPELLER have been reduced in the background and the scanning time has been reduced. I think the whole spine examination will be effective with AIR™ Recon."
Overall, AIR™ on the SIGNA™ Pioneer system has positively impacted clinical confidence throughout the hospital.
"SIGNA™ Pioneer with AIR™ is considered to be the best system we have because it can flexibly handle various examinations."
Dr. Takayuki Masui