‡Not licensed in accordance with Canadian law. Not available for sale in Canada. Not CE marked. Not available for sale in all regions.
‡Not licensed in accordance with Canadian law. Not available for sale in Canada. Not CE marked. Not available for sale in all regions.
Not licensed in accordance with Canadian law. Not available for sale in Canada. Not CE marked. Not available for sale in all regions.
‡Not licensed in accordance with Canadian law. Not available for sale in Canada. Not CE marked. Not available for sale in all regions.
‡Not licensed in accordance with Canadian law. Not available for sale in Canada. Not CE marked. Not available for sale in all regions.
A
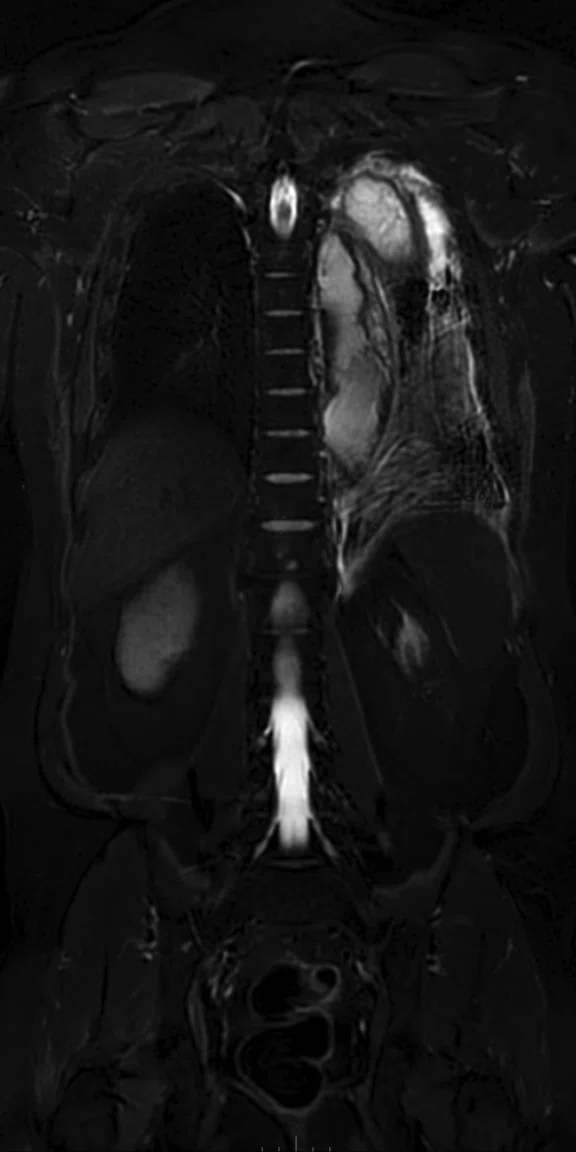
Figure 2.
(A) Coronal T2w STIR PROPELLER MB; (B) Coronal LAVA; (C) Coronal DW-EPI, 2 stations; (D) whole-body DWI, radial MIP; (E) whole-body Coronal DWI radial MIP, 2 stations.
B
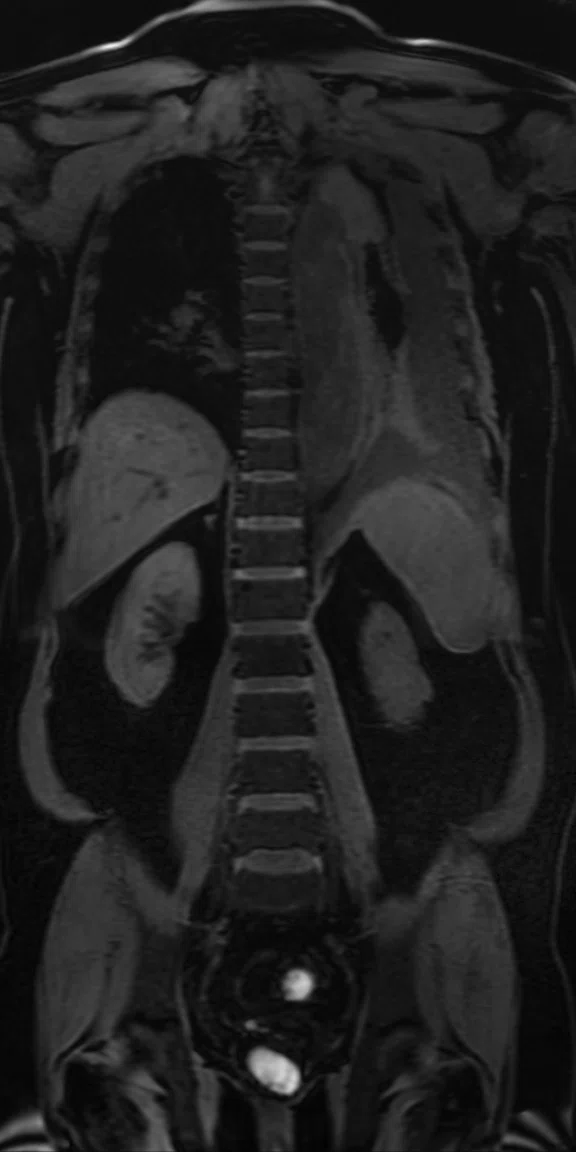
Figure 2.
(A) Coronal T2w STIR PROPELLER MB; (B) Coronal LAVA; (C) Coronal DW-EPI, 2 stations; (D) whole-body DWI, radial MIP; (E) whole-body Coronal DWI radial MIP, 2 stations.
C
Figure 2.
(A) Coronal T2w STIR PROPELLER MB; (B) Coronal LAVA; (C) Coronal DW-EPI, 2 stations; (D) whole-body DWI, radial MIP; (E) whole-body Coronal DWI radial MIP, 2 stations.
D
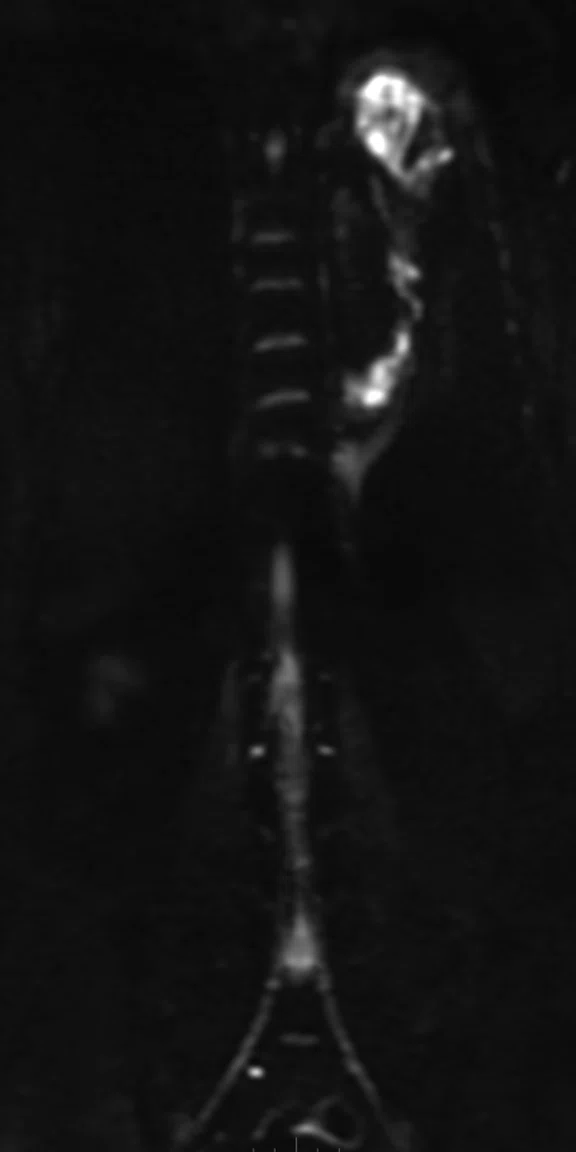
Figure 2.
(A) Coronal T2w STIR PROPELLER MB; (B) Coronal LAVA; (C) Coronal DW-EPI, 2 stations; (D) whole-body DWI, radial MIP; (E) whole-body Coronal DWI radial MIP, 2 stations.
E
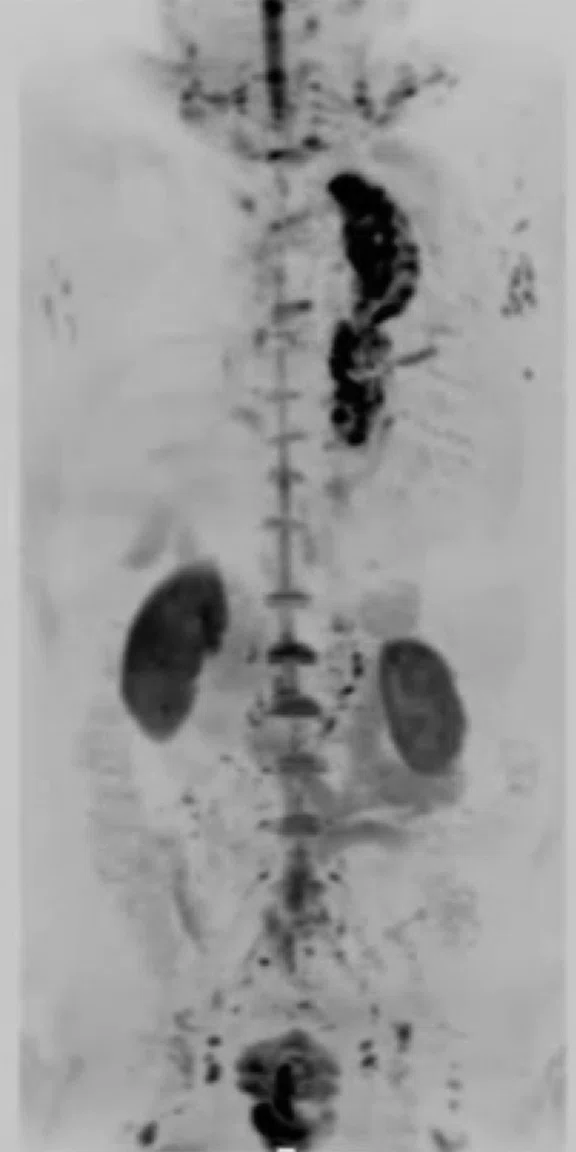
Figure 2.
(A) Coronal T2w STIR PROPELLER MB; (B) Coronal LAVA; (C) Coronal DW-EPI, 2 stations; (D) whole-body DWI, radial MIP; (E) whole-body Coronal DWI radial MIP, 2 stations.
A
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
B
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
C
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
D
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
E
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
F
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
A
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
D
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
B
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
E
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
C
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
F
Figure 1.
With the improvement in resolution using MUSE, there is clear depiction of the infarct in the gray matter compared to the conventional sequence. (A-C) Conventional DWI, b1000; (D-F) MUSE, b1000.
result


PREVIOUS
${prev-page}
NEXT
${next-page}
Subscribe Now
Manage Subscription
FOLLOW US
Contact Us • Cookie Preferences • Privacy Policy • California Privacy PolicyDo Not Sell or Share My Personal Information • Terms & Conditions • Security
© 2024 GE HealthCare. GE is a trademark of General Electric Company. Used under trademark license.
CASE STUDIES
Diffusion imaging with AIR Technology Suite
Diffusion imaging with AIR Technology Suite
Submitted by Kawasaki Saiwai Hospital
CASE STUDIES
Diffusion imaging with AIR Technology Suite
Diffusion imaging with AIR Technology Suite
Submitted by Kawasaki Saiwai Hospital
Case 1
A 59-year-old female with loss of consciousness. Prior history includes gall bladder stone and cholecystitis.
MR findings
Patient has multiple infarction. Micro infarction was not clearly visualized in conventional DWI sequence. However, MUSE enabled high-resolution DWI that enabled depiction of micro infarction in the gray matter.
Case 2
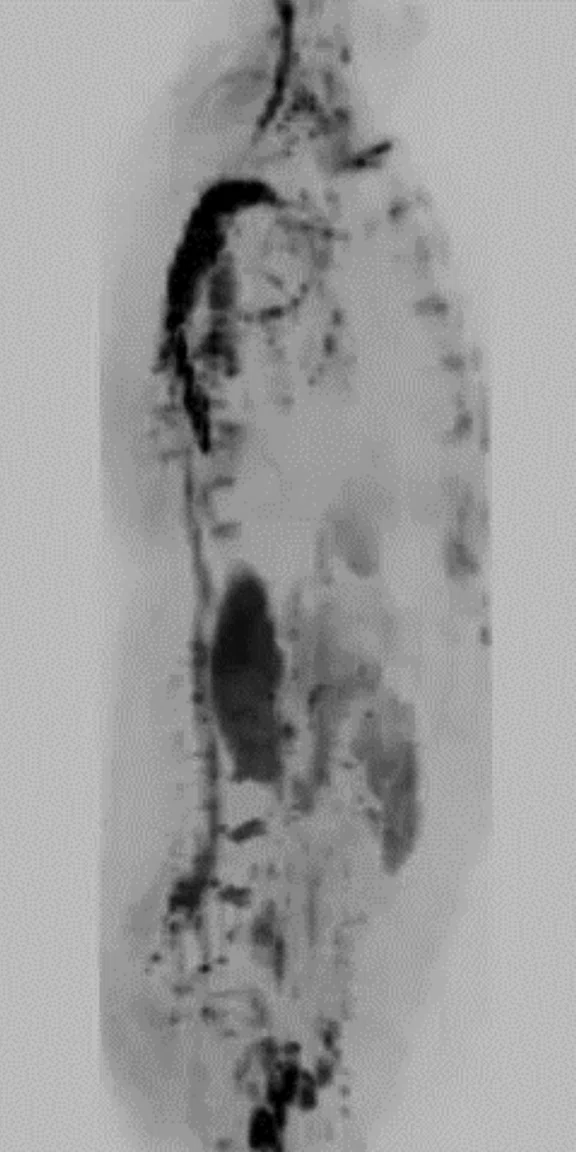
A 46-year-old male presenting with fever of unknown origin and suspected infection after aortic stent replacement surgery.
MR findings
T2 SSFSE and T2 STIR PROPELLER MB confirmed abscess formation in the left upper lung lobe without having to reposition the coil. High signal DWI confirmed location. Whole-body Coronal DWI was acquired in two stations. The AIR Technology™‡ Anterior Array (AA) allows higher parallel imaging factors, enabling low-distortion DWI even in cases with a large field-of-view.
Case 2
A 46-year-old male presenting with fever of unknown origin and suspected infection after aortic stent replacement surgery.
MR findings
T2 SSFSE and T2 STIR PROPELLER MB confirmed abscess formation in the left upper lung lobe without having to reposition the coil. High signal DWI confirmed location. Whole-body Coronal DWI was acquired in two stations. The AIR Technology™‡ Anterior Array (AA) allows higher parallel imaging factors, enabling low-distortion DWI even in cases with a large field-of-view.

Case 1
A 59-year-old female with loss of consciousness. Prior history includes gall bladder stone and cholecystitis.
MR findings
Patient has multiple infarction. Micro infarction was not clearly visualized in conventional DWI sequence. However, MUSE enabled high-resolution DWI that enabled depiction of micro infarction in the gray matter.