result
A
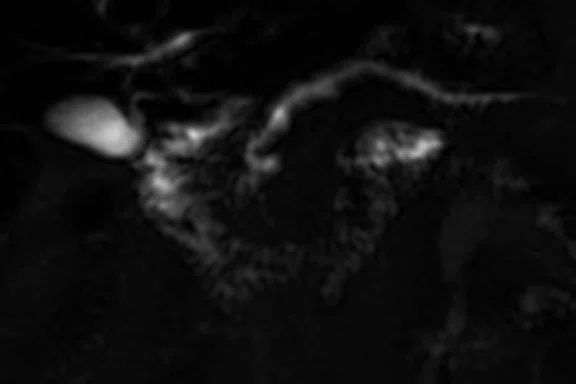
Figure 1.
2D MRCP of a 91-year-old patient with dementia. (A) Conventional reconstruction, (B) with AIR™ Recon DL.
Images courtesy of Melany Atkins, MD, Fairfax Radiology Centers.
B
Figure 1.
2D MRCP of a 91-year-old patient with dementia. (A) Conventional reconstruction, (B) with AIR™ Recon DL.
Images courtesy of Melany Atkins, MD, Fairfax Radiology Centers.
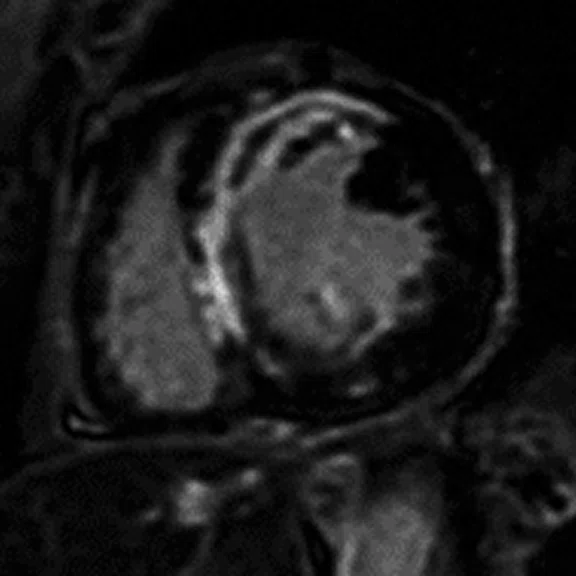
A
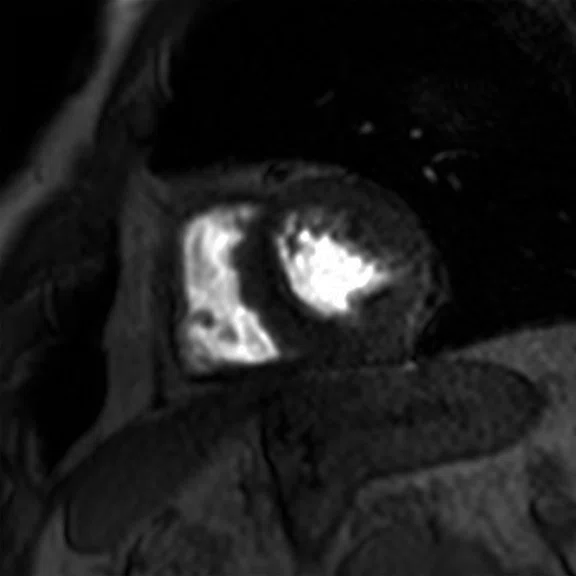
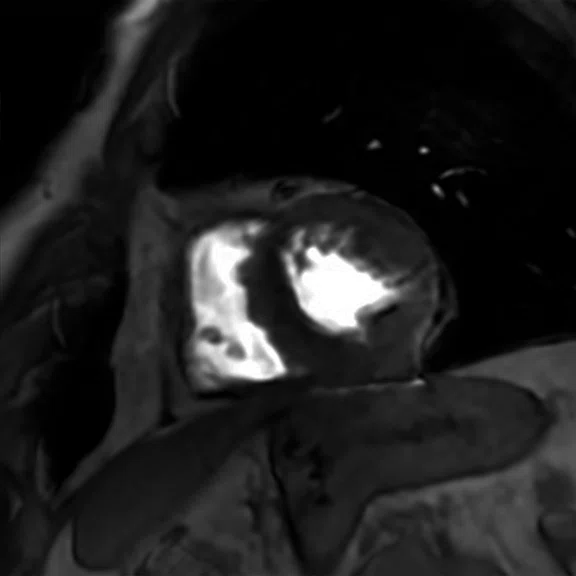
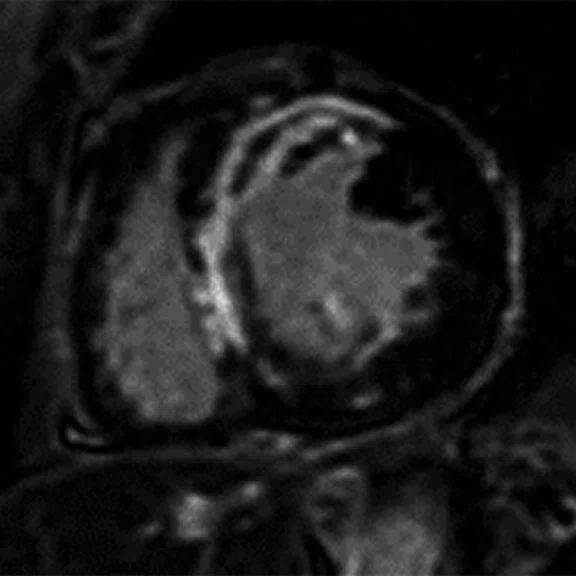
Figure 2.
Cardiac exam. (A, B) Time course perfusion with (A) conventional and (B) AIRTM Recon DL reconstruction. (C,D) Short axis MDE with (C) conventional and (D) AIRTM Recon DL reconstruction.
Images courtesy of Christopher Ahlers, MD, radiomed.
B
Figure 2.
Cardiac exam. (A, B) Time course perfusion with (A) conventional and (B) AIRTM Recon DL reconstruction. (C,D) Short axis MDE with (C) conventional and (D) AIRTM Recon DL reconstruction.
Images courtesy of Christopher Ahlers, MD, radiomed.
C
Figure 2.
Cardiac exam. (A, B) Time course perfusion with (A) conventional and (B) AIRTM Recon DL reconstruction. (C,D) Short axis MDE with (C) conventional and (D) AIRTM Recon DL reconstruction.
Images courtesy of Christopher Ahlers, MD, radiomed.
D
Figure 2.
Cardiac exam. (A, B) Time course perfusion with (A) conventional and (B) AIRTM Recon DL reconstruction. (C,D) Short axis MDE with (C) conventional and (D) AIRTM Recon DL reconstruction.
Images courtesy of Christopher Ahlers, MD, radiomed.
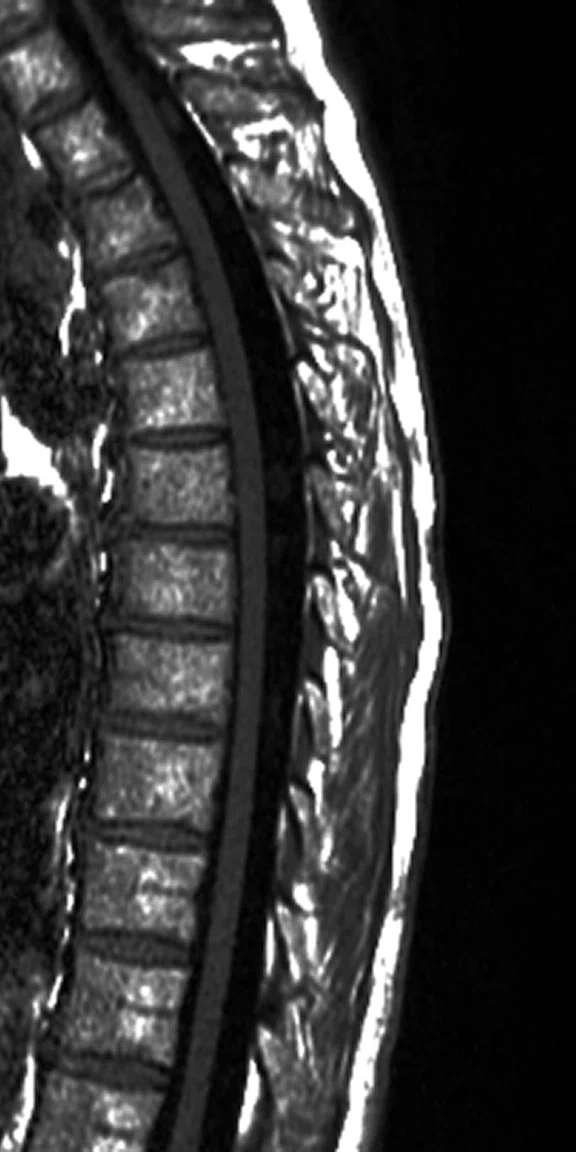
A
Figure 3.
T-spine sagittal T1 FLAIR, 1.2 x 1.0 x 3 mm, 1:04 min. Same acquisition with (A) conventional reconstruction with low SNR and (B) improved SNR using AIRTM Recon DL.
Images courtesy of Lawrence Tanenbaum, MD, RadNet, Inc.
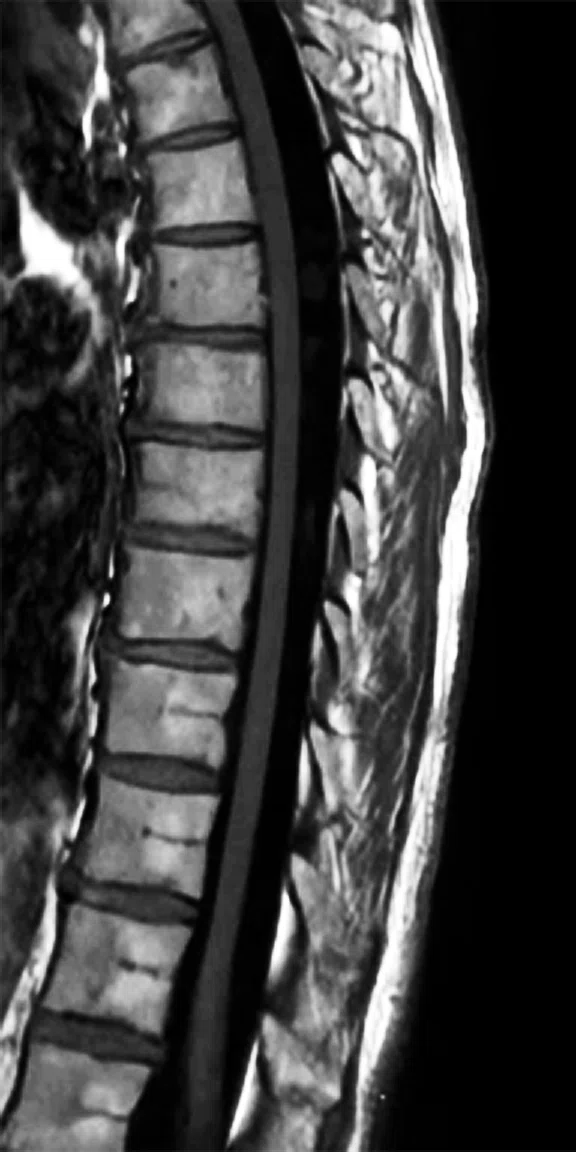
B
Figure 3.
T-spine sagittal T1 FLAIR, 1.2 x 1.0 x 3 mm, 1:04 min. Same acquisition with (A) conventional reconstruction with low SNR and (B) improved SNR using AIRTM Recon DL.
Images courtesy of Lawrence Tanenbaum, MD, RadNet, Inc.
A-1
Figure 4.
AIR™ Recon DL improves resolution and SNR and decreases scan time. (A, B) Conventional reconstruction in January 2020 and (C, D) with AIR™ Recon DL in October 2020. (A) Coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 3:08 min.; (B) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.7 x 2.0 mm, 3:18 min.; (C) coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 1:14 min.; and (D) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.6 x 2.0 mm, 1:48 min.
B-1
Figure 4.
AIR™ Recon DL improves resolution and SNR and decreases scan time. (A, B) Conventional reconstruction in January 2020 and (C, D) with AIR™ Recon DL in October 2020. (A) Coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 3:08 min.; (B) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.7 x 2.0 mm, 3:18 min.; (C) coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 1:14 min.; and (D) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.6 x 2.0 mm, 1:48 min.
C-1
Figure 4.
AIR™ Recon DL improves resolution and SNR and decreases scan time. (A, B) Conventional reconstruction in January 2020 and (C, D) with AIR™ Recon DL in October 2020. (A) Coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 3:08 min.; (B) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.7 x 2.0 mm, 3:18 min.; (C) coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 1:14 min.; and (D) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.6 x 2.0 mm, 1:48 min.
D-1
Figure 4.
AIR™ Recon DL improves resolution and SNR and decreases scan time. (A, B) Conventional reconstruction in January 2020 and (C, D) with AIR™ Recon DL in October 2020. (A) Coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 3:08 min.; (B) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.7 x 2.0 mm, 3:18 min.; (C) coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 1:14 min.; and (D) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.6 x 2.0 mm, 1:48 min.
A-2
Figure 4.
AIR™ Recon DL improves resolution and SNR and decreases scan time. (A, B) Conventional reconstruction in January 2020 and (C, D) with AIR™ Recon DL in October 2020. (A) Coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 3:08 min.; (B) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.7 x 2.0 mm, 3:18 min.; (C) coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 1:14 min.; and (D) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.6 x 2.0 mm, 1:48 min.
B-2
Figure 4.
AIR™ Recon DL improves resolution and SNR and decreases scan time. (A, B) Conventional reconstruction in January 2020 and (C, D) with AIR™ Recon DL in October 2020. (A) Coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 3:08 min.; (B) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.7 x 2.0 mm, 3:18 min.; (C) coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 1:14 min.; and (D) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.6 x 2.0 mm, 1:48 min.
C-2
Figure 4.
AIR™ Recon DL improves resolution and SNR and decreases scan time. (A, B) Conventional reconstruction in January 2020 and (C, D) with AIR™ Recon DL in October 2020. (A) Coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 3:08 min.; (B) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.7 x 2.0 mm, 3:18 min.; (C) coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 1:14 min.; and (D) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.6 x 2.0 mm, 1:48 min.
D-2
Figure 4.
AIR™ Recon DL improves resolution and SNR and decreases scan time. (A, B) Conventional reconstruction in January 2020 and (C, D) with AIR™ Recon DL in October 2020. (A) Coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 3:08 min.; (B) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.7 x 2.0 mm, 3:18 min.; (C) coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 1:14 min.; and (D) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.6 x 2.0 mm, 1:48 min.


PREVIOUS
${prev-page}
NEXT
${next-page}
Subscribe Now
Manage Subscription
FOLLOW US
Contact Us • Cookie Preferences • Privacy Policy • California Privacy PolicyDo Not Sell or Share My Personal Information • Terms & Conditions • Security
© 2024 GE HealthCare. GE is a trademark of General Electric Company. Used under trademark license.
SPOTLIGHT
Intelligently efficient deep-learning reconstruction in MR
Intelligently efficient deep-learning reconstruction in MR
Artificial intelligence (AI) applications in the field of medical imaging are no longer just conceptual. They are currently proving their value in clinical practice, for example, offering clinicians assistance in triaging and prioritizing urgent cases in X-Ray, using deep learning to improve the quality of low-dose CT scans, and applying deep-learning models for image reconstruction in MR.
Artificial intelligence (AI) applications in the field of medical imaging are no longer just conceptual. They are currently proving their value in clinical practice, for example, offering clinicians assistance in triaging and prioritizing urgent cases in X-Ray, using deep learning to improve the quality of low-dose CT scans, and applying deep-learning models for image reconstruction in MR.
A recent webinar hosted by GE Healthcare, "Intelligently Efficient – Brought to you by AIR™ Recon DL," featured a panel of clinicians who discussed some of the ways that AI has impacted MR cases clinically, and improved productivity and return on investment (ROI) in their overall imaging operations and workflow.
Applying AI and deep-learning (DL) algorithms to MR image reconstruction is enabling improvements in MR that were not possible using traditional reconstruction methods. Healthcare providers are using this technology to produce high-quality images with shorter scan times, overcoming the historical trade-offs in MR between scan time and image quality.
Expert panelists who participated in the webinar are using GE’s AIR™ Recon DL technology, which is a deep-learningtrained algorithm to reconstruct sharper images. AIR™ Recon DL leverages all of the raw acquisition data, delivers a higher SNR with user-selectable improvement levels, and is compatible with all anatomies.
Melany Atkins, MD, a radiologist with Fairfax Radiology Centers in Fairfax, Virginia, has been able to improve image quality and resolution in body imaging using AIR™ Recon DL. Dr. Atkins is also shortening the traditionally longer acquisition times for her patients’ pelvic and abdominal exams.
For example, in the case of a 91-year old patient with dementia who really struggled in the MR scanner, Dr. Atkins tried to do rapid MRCP imaging using AIR™ Recon DL and observed significant image quality improvement.
"We can all appreciate significant improvement in image quality, all the way to the ampulla, with the utilization of AIR™ Recon DL," says Dr. Atkins (Figure 1).
In study after study, Dr. Atkins noted that her patients are spending less time on the table, and she is getting far superior image quality to inform clinical decisions on diagnosis and treatment. Her colleagues have also embraced the use of AIR™ Recon DL for all musculoskeletal and neuroimaging based on her clinical results.
"One of the things we struggle with in a small field-of-view, such as pelvic imaging, with super high resolution is long scan times," explained Dr. Atkins. "Before we had AIR™ Recon DL, we often had 5-6 minute, high-resolution T2 sequences that often led to organ blur because of patient motion.
"[With AIR™ Recon DL for small FOV pelvic imaging] we decreased our NEX (number of excitations) to two, and we’ve got just over 2.5 minute acquisition time… but no issues with organ blur. And I think we can all appreciate that the image quality utilizing AIR™ Recon DL in a third of the time is really far superior."
Dr. Melany Atkins
Protocol optimization for every imaging scenario
As Dr. Atkins demonstrated, the application of deep-learning reconstruction to traditional MR imaging has resulted in superior image quality while reducing a patient’s time in the scanner. Christopher Ahlers, MD, a radiologist and managing partner at radiomed Practice for Radiology and Nuclear Medicine in Wiesbaden, Germany, noted that these types of clinical results are not only possible, but also extremely easy to achieve with AIR™ Recon DL. He added that this DL-based solution can be incorporated seamlessly into clinical practice without additional work for the radiologist.
"Mostly, it’s about protocol optimization," Dr. Ahlers explained. "When we optimize the original sequence to increase spatial resolution or improve scan time – such as reducing the number of excitations – we likely introduce some noise on the images. This noise can be removed by using AIR™ Recon DL in order to regain signal we lost or even improve SNR. Our observation is that we can drastically increase the contrast-to-noise ratio, which really improves lesion conspicuity.
"AIR™ Recon DL allows us to push protocols or applications to levels that would otherwise be incompatible with conventional reconstruction and it works in any anatomy. It is easy to switch on AIR™ Recon DL – you just select the preferred SNR level from the drop-down menu."
Dr. Christopher Ahlers
Changes in MR workflow productivity
While the clinical images illustrate the dynamic improvement in image quality achieved by using deep-learning image reconstruction, another clinician shared the equally impressive quantitative performance results he has achieved by incorporating AIR™ Recon DL into his MR workflows.
Lawrence Tanenbaum, MD, FACR, Vice President and Medical Director, MRI, CT and Advanced Imaging for RadNet, Inc., a national outpatient imaging provider with more than 300 centers in its network, is using deep-learning reconstruction at one of RadNet’s busiest centers in Manhattan.
"Initially, you think this will help me go faster, and it does, but it’s actually going to elevate your entire imaging chain because there’s such powerful noise reduction and greater efficiency," Dr. Tanenbaum said (Figure 3).
"Across the board, and across the range of exams, we run anywhere between 30% and 50% reduction in scan times. We originally had 20-minute scan time slots; now we changed to 15-minute slots. This change allows us to add one more patient each hour, which translates to 10 more patients each day."
Dr. Lawrence Tanenbaum
Aside from the throughput benefits, there is improved operational consistency, Dr. Tanenbaum added. "It allows us to stay on schedule, reduce overtime needs, and gives us a greater ability to accommodate add-ons and handle the typical disruptions that will always come up, like insurance certifications and implanted devices."
The impact on ROI
Randall Stenoien, MD, ABR, offered a perspective from a private radiology practice. As owner and CEO of Houston Medical Imaging, Dr. Stenoien commented that investing in new technology, especially expensive technology, needs to be very thoughtful. It’s a business decision.
"I found that in my practice, the secret to my financial survival has been the fact that we’re able to do more complex exams," he explained. "There is more reimbursement there. The downside is that these exams are substantially more time-intensive and the scheduling slots need to be much longer."
Dr. Stenoien made the decision to invest in opening a new imaging center in October 2019 with a 12-month timeline to profitability based on revenue projections. Unfortunately, because of the COVID-19 pandemic, he was forced to close the center in March 2020. When Dr. Stenoien heard about the potential of deep-learning reconstruction in MR with AIR™ Recon DL to accelerate image acquisition, he was intrigued. Then he saw the image quality.
"The image quality was fantastic immediately," he explained. He was able to quickly implement the solution with on-site GE applications support – he didn’t need to close down the center for training.
"And we were seeing dramatic reduction in scan times," Dr. Stenoien says. "One of our first patients was a pituitary scan whose prior exam in January 2020 took 30 minutes and 40 seconds. The patient returned in October 2020 on the same scanner using AIR™ Recon DL and the exam was 14 minutes and 42 seconds – a 52% reduction. And when I sent those images to my neuroradiologist, I immediately got a phone call to ask what in the world had happened. It was the prettiest pituitary scan she’d ever seen." (See Figure 4.)
Figure 4.
AIR™ Recon DL improves resolution and SNR and decreases scan time. (A, B) Conventional reconstruction in January 2020 and (C, D) with AIR™ Recon DL in October 2020. (A) Coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 3:08 min.; (B) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.7 x 2.0 mm, 3:18 min.; (C) coronal T2, 0.5 x 0.5 x 2.0 mm, 1:14 min.; and (D) sagittal T1 post contrast, 0.5 x 0.6 x 2.0 mm, 1:48 min.
Dr. Stenoien added that the learning curve to adopt AIR™ Recon DL was so rapid that his team was able to immediately adapt their protocols and increase their patient load by 50%. He spoke about the financial impact of his investment, especially considering the global pandemic. In many cases, it takes nearly as long to prep and position the patient and then get them back off the table and clean the room as it does to perform the scan.
"How did this affect our profitability? To me, that’s the most compelling part of the story. We went live at the end of September 2020, and prior to that, we were averaging 10-12 patients a day.
"With AIR™ Recon DL, we were able to add four time slots a day on average, and the reimbursement data, it’s not linear. October of 2020 was the first month we went into the black. We not only broke even, but we were able to see a return on investment. As we come out of COVID and increase volumes further, we’re going to have a really tremendous opportunity to be profitable. It’s been a wonderful experience."
Dr. Randall Stenoien
With results like Dr. Stenoin’s and those discussed earlier, it’s clear that AI-enabled technologies hold great promise for MR. In the case of GE’s AIR™ Recon DL, whether it’s increasing SNR, reducing scan times, enabling greater patient throughput or boosting ROI, this deep-learning tool stands to bring substantial benefits to practices, physicians and patients alike.

To view the webinar and compelling images enabled by AIR™ Recon DL, visit: tinyurl.com/intelligentlyefficient