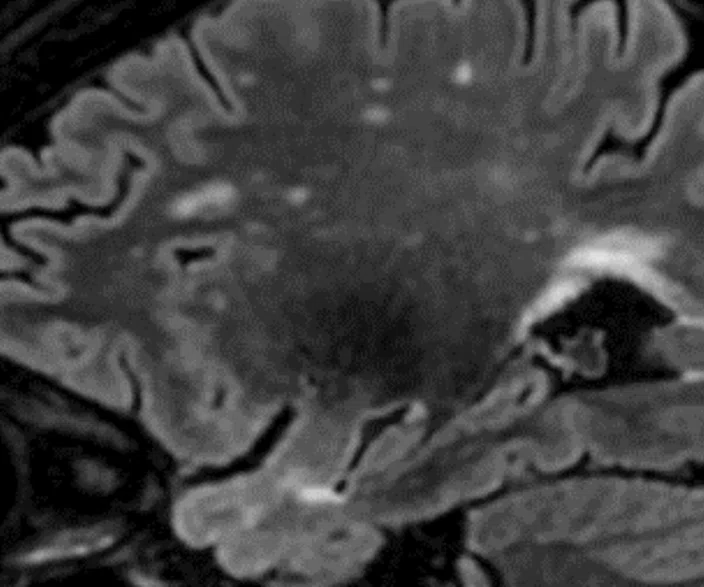
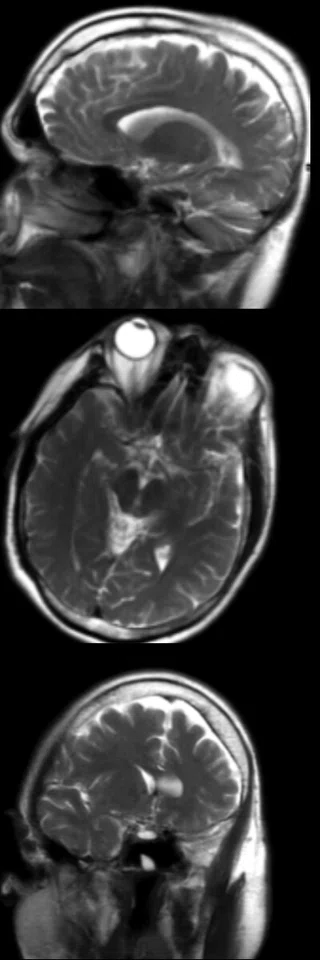
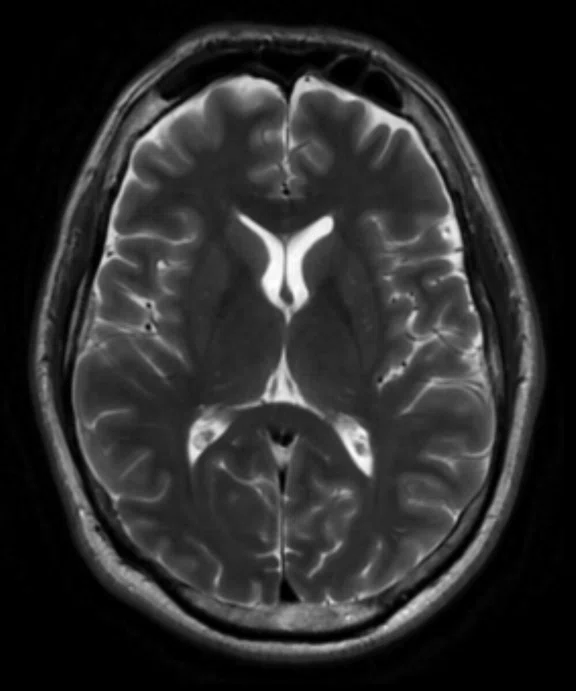
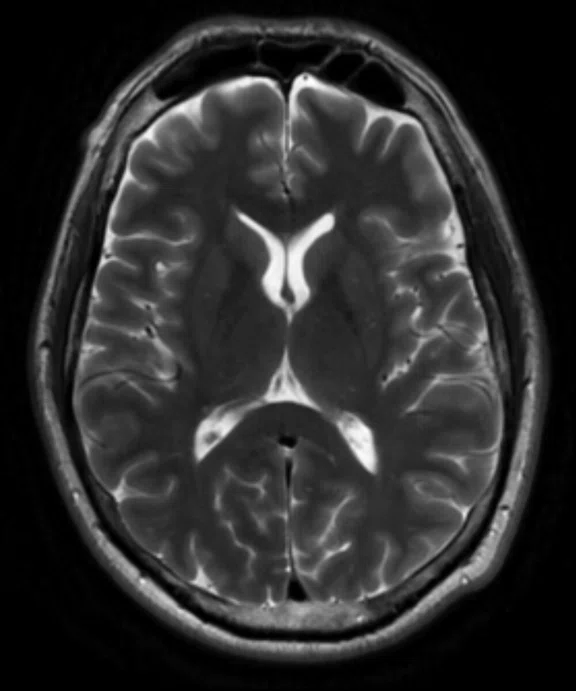
Sagittal Cube T2 FLAIR and coronal
MPR with HyperSense
1 x 1.1 x 1.2 mm
3:30 min.
The AIR™ 48ch Head Coil, available on all 3.0T GE MR scanners, provides excellent SNR and uniformity as demonstrated in a patient with Multiple Sclerosis (above). Cervical spine imaging with FSE Flex and carotid. Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
Sagittal Cube T2 FLAIR and coronal
MPR with HyperSense
1 x 1.1 x 1.2 mm
3:30 min.
The AIR™ 48ch Head Coil, available on all 3.0T GE MR scanners, provides excellent SNR and uniformity as demonstrated in a patient with Multiple Sclerosis (above). Cervical spine imaging with FSE Flex and carotid. Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
The AIR™ 48ch Head Coil, available on all 3.0T GE MR scanners, provides excellent SNR and uniformity as demonstrated in a patient with Multiple Sclerosis (above). Cervical spine imaging with FSE Flex and carotid. Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
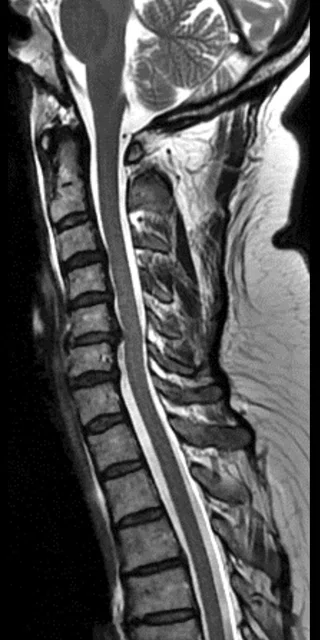
Sagittal T2 FSE
0.7 x 0.8 x 3 mm
The AIR™ 48ch Head Coil, available on all 3.0T GE MR scanners, provides excellent SNR and uniformity as demonstrated in a patient with Multiple Sclerosis. Cervical spine imaging with FSE Flex and carotid (above). Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
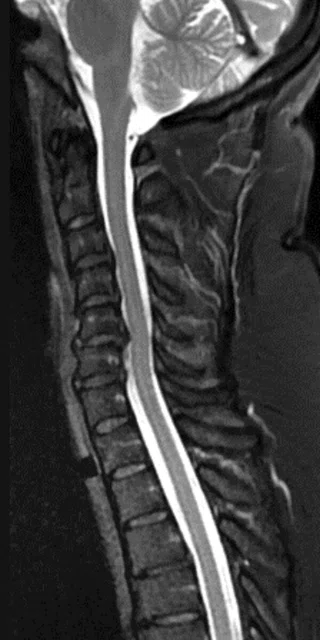
Sagittal T2 FSE Flex
0.9 x 0.9 x 3 mm
The AIR™ 48ch Head Coil, available on all 3.0T GE MR scanners, provides excellent SNR and uniformity as demonstrated in a patient with Multiple Sclerosis. Cervical spine imaging with FSE Flex and carotid (above). Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
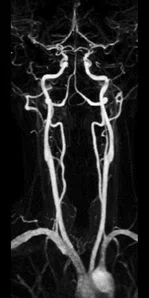
ceMRA
0.9 x 0.9 x 1.2 mm
The AIR™ 48ch Head Coil, available on all 3.0T GE MR scanners, provides excellent SNR and uniformity as demonstrated in a patient with Multiple Sclerosis. Cervical spine imaging with FSE Flex and carotid (above). Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
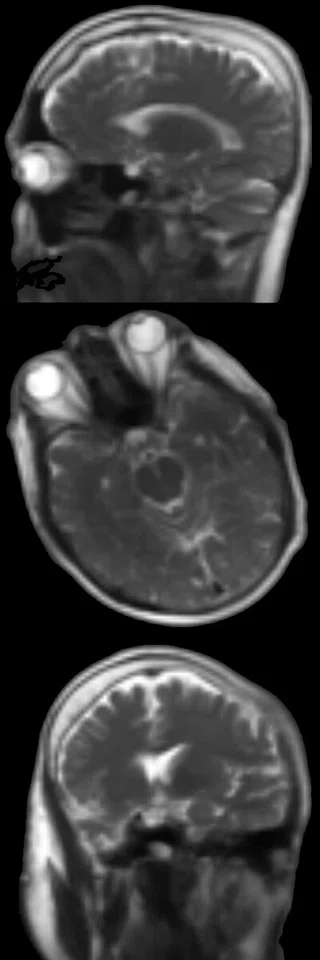
3 plane localizer
Using a deep-learning algorithm trained on tens of thousands of images, AIR x™ revolutionizes the workflow for brain exams. It automatically prescribes slices to help drive consistency and reproducibility regardless of user, patient age, pathology or patient position in the magnet. Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
Using a deep-learning algorithm trained on tens of thousands of images, AIR x™ revolutionizes the workflow for brain exams. It automatically prescribes slices to help drive consistency and reproducibility regardless of user, patient age, pathology or patient position in the magnet. Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
3 plane localizer
Using a deep-learning algorithm trained on tens of thousands of images, AIR x™ revolutionizes the workflow for brain exams. It automatically prescribes slices to help drive consistency and reproducibility regardless of user, patient age, pathology or patient position in the magnet. Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
Using a deep-learning algorithm trained on tens of thousands of images, AIR x™ revolutionizes the workflow for brain exams. It automatically prescribes slices to help drive consistency and reproducibility regardless of user, patient age, pathology or patient position in the magnet. Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
result


PREVIOUS
${prev-page}
NEXT
${next-page}
Subscribe Now
Manage Subscription
FOLLOW US
Contact Us • Cookie Preferences • Privacy Policy • California Privacy PolicyDo Not Sell or Share My Personal Information • Terms & Conditions • Security
© 2024 GE HealthCare. GE is a trademark of General Electric Company. Used under trademark license.
Sagittal Cube T2 FLAIR and coronal
MPR with HyperSense
1 x 1.1 x 1.2 mm
3:30 min.
The AIR™ 48ch Head Coil, available on all 3.0T GE MR scanners, provides excellent SNR and uniformity as demonstrated in a patient with Multiple Sclerosis (above). Cervical spine imaging with FSE Flex and carotid (images below).
Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland
Using a deep-learning algorithm trained on tens of thousands of images, AIR x™ revolutionizes the work ow for brain exams. It automatically prescribes slices to help drive consistency and reproducibility regardless of user, patient age, pathology or patient position in the magnet. Images courtesy of RNR, Zurich, Switzerland