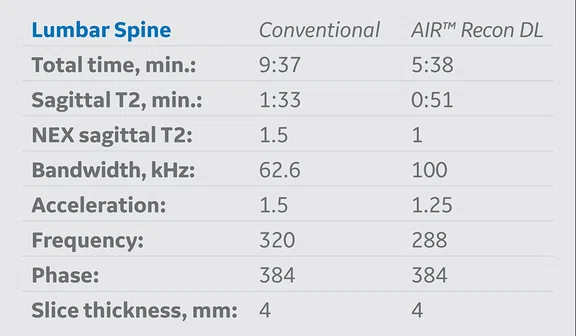
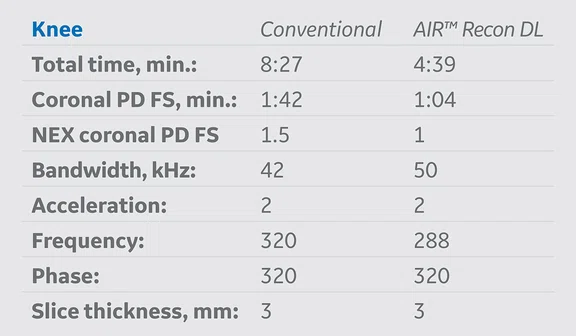
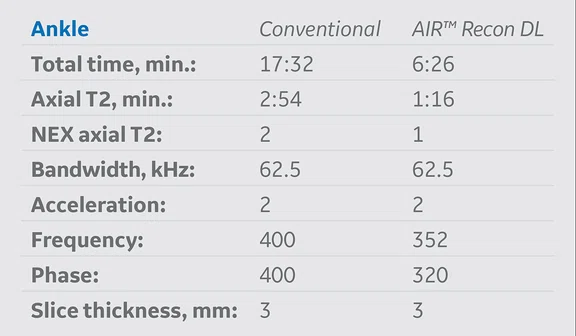
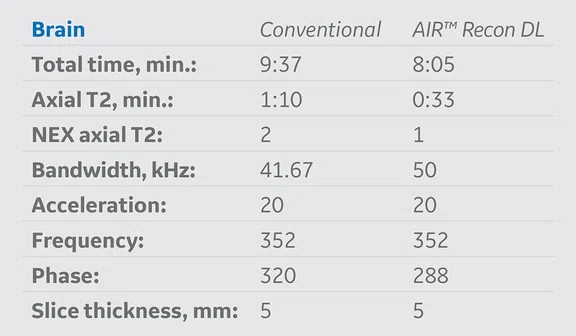
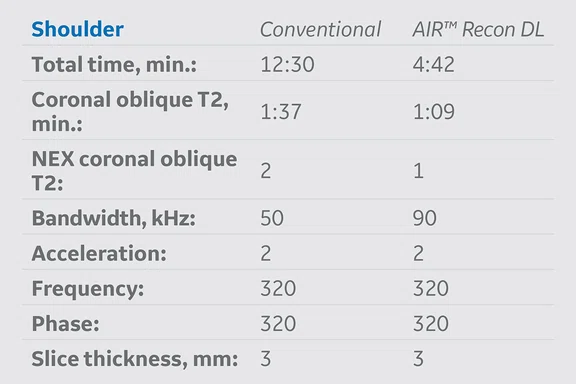
Table 1.
MR protocol implementation of AIR™ Recon DL versus conventional acquisition protocols. The average exam time reduction of all protocols where AIR™ Recon DL was applied was approximately 48% and the average schedule time reduction was nearly 40%.
A
Figure 3.
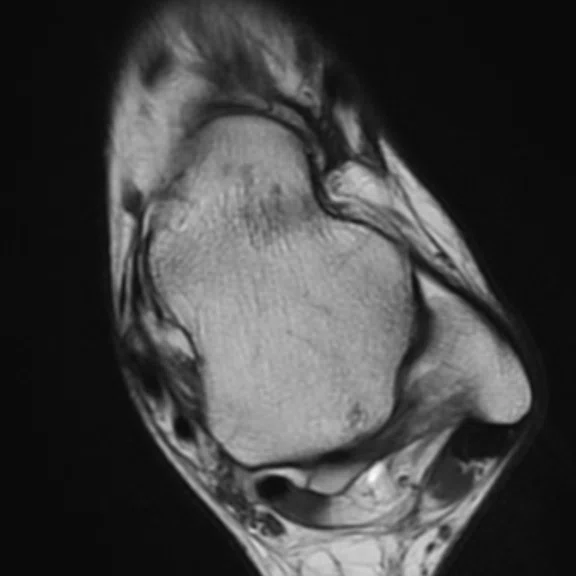
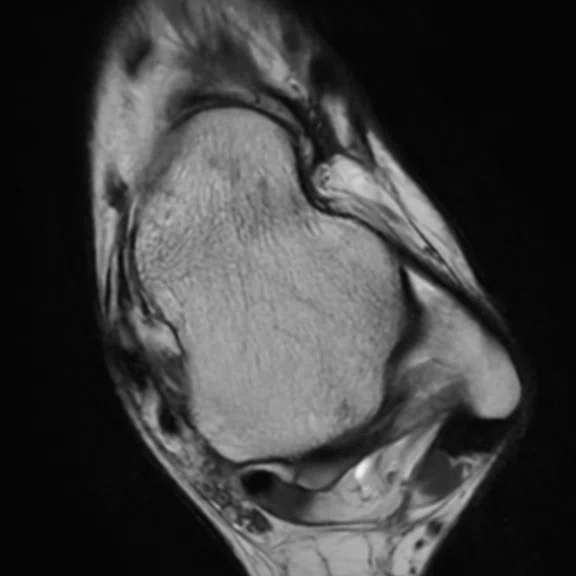
A 36-year-old male with pain in the external malleolar. (A) Conventional and (B) AIR™ Recon DL.
B
Figure 3.
A 36-year-old male with pain in the external malleolar. (A) Conventional and (B) AIR™ Recon DL.
A
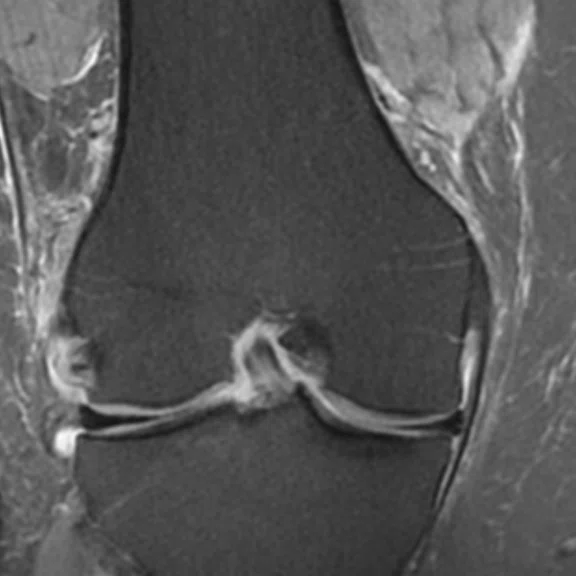
Figure 2.
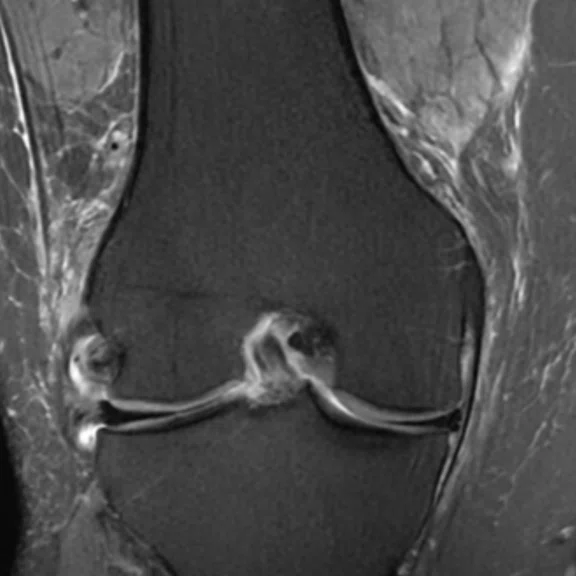
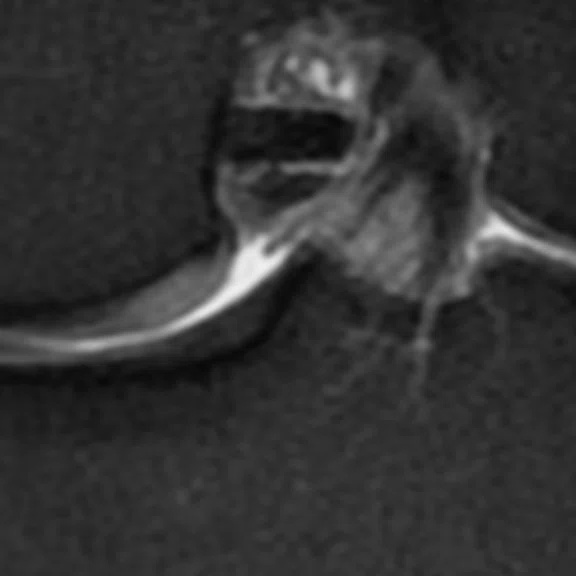
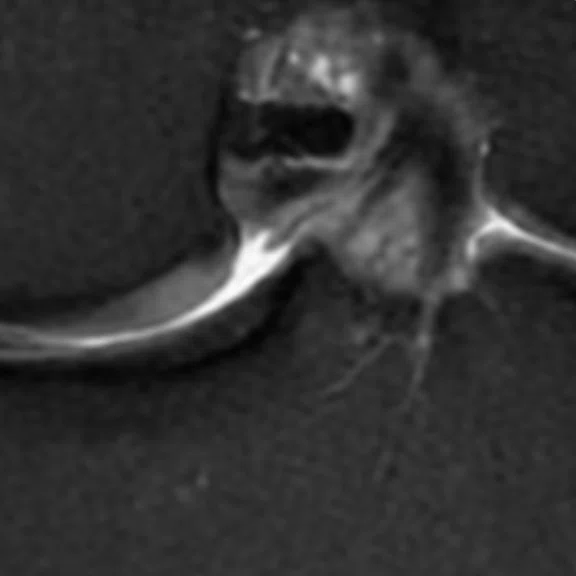
(A, B) A 42-year-old male patient with gonalgia during exercise. (C, D) A 28-year-old male patient with gonalgia during exercise. (A, C) Conventional and (B, D) AIR™ Recon DL.
B
Figure 2.
(A, B) A 42-year-old male patient with gonalgia during exercise. (C, D) A 28-year-old male patient with gonalgia during exercise. (A, C) Conventional and (B, D) AIR™ Recon DL.
C
Figure 2.
(A, B) A 42-year-old male patient with gonalgia during exercise. (C, D) A 28-year-old male patient with gonalgia during exercise. (A, C) Conventional and (B, D) AIR™ Recon DL.
D
Figure 2.
(A, B) A 42-year-old male patient with gonalgia during exercise. (C, D) A 28-year-old male patient with gonalgia during exercise. (A, C) Conventional and (B, D) AIR™ Recon DL.
A
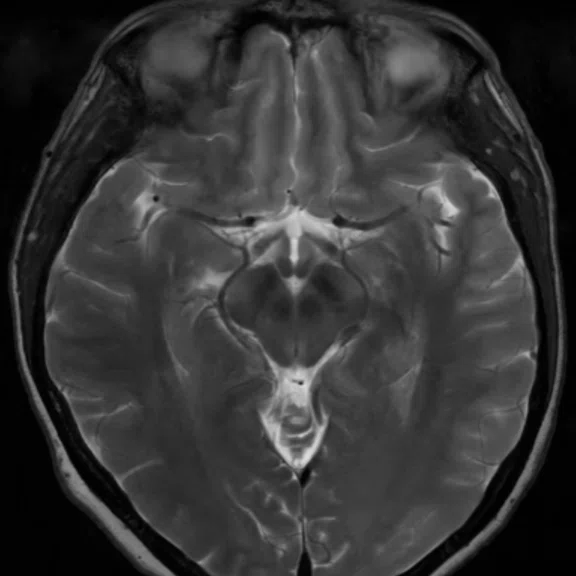
Figure 4.
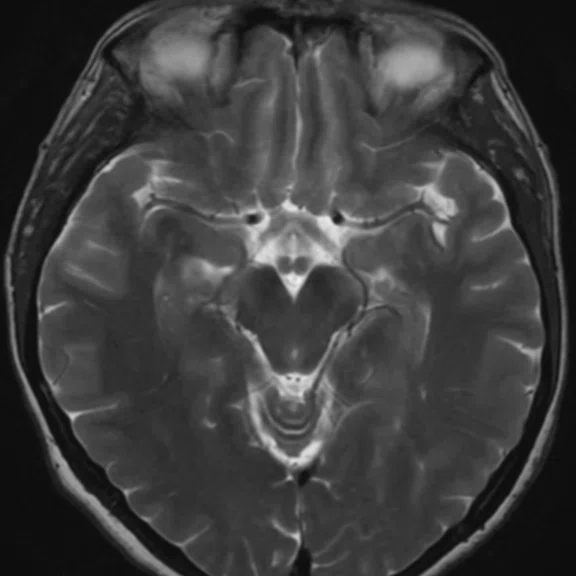
A 48-year-old male patient with cephalea. (A) Conventional and (B) AIR™ Recon DL (2D sequences only).
B
Figure 4.
A 48-year-old male patient with cephalea. (A) Conventional and (B) AIR™ Recon DL (2D sequences only).
Table 3.
Image quality results. AIR™ Recon DL reconstructed image quality was rated higher than conventional reconstructed images (w/o AIR™ Recon DL), 2.5 and 2.3, respectively.
A
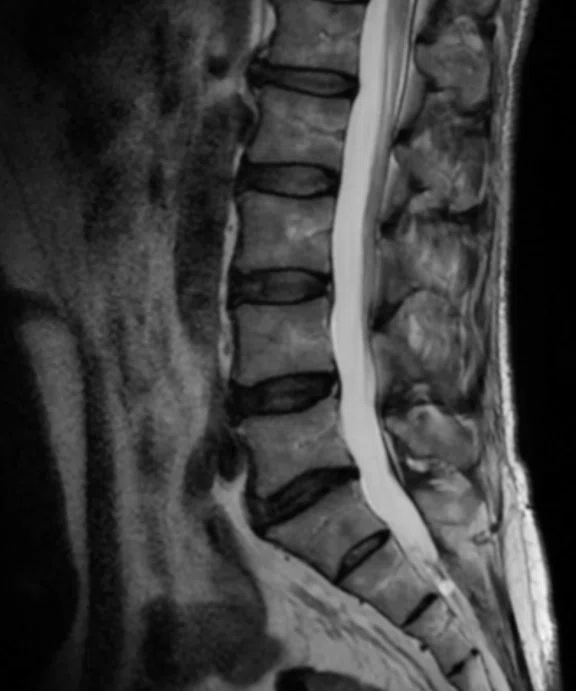
Figure 1.
A 45-year-old male patient with lumbar pain. (A) Conventional and (B) AIR™ Recon DL.
B
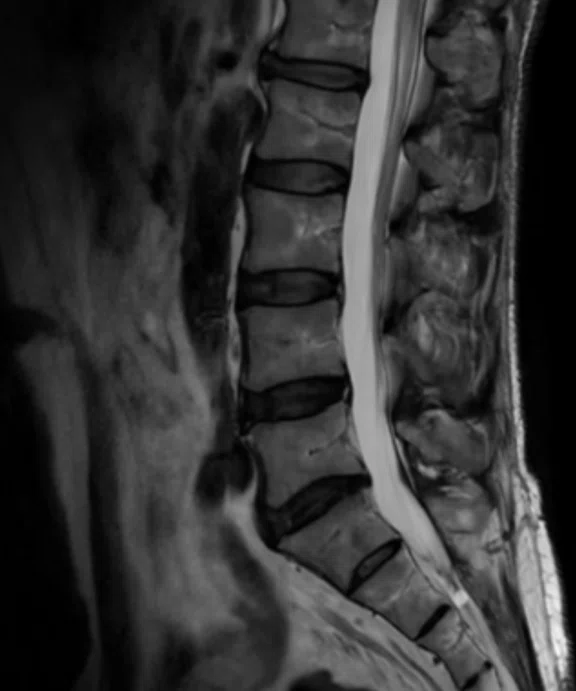
Figure 1.
A 45-year-old male patient with lumbar pain. (A) Conventional and (B) AIR™ Recon DL.
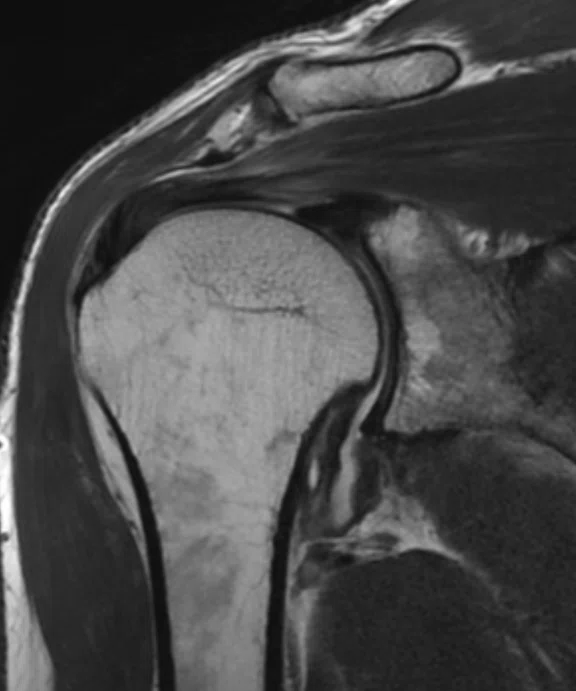
A
Figure 5.
A 53-year-old female patient with rotator cuff syndrome. (A) Conventional and (B) AIR™ Recon DL.
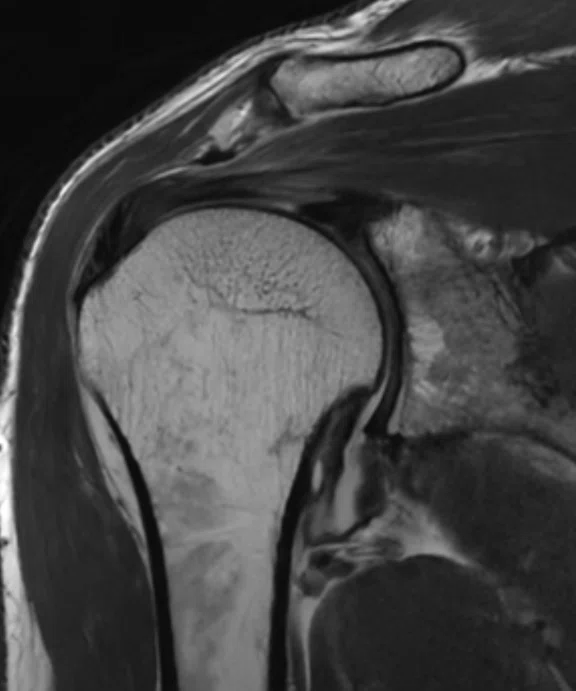
B
Figure 5.
A 53-year-old female patient with rotator cuff syndrome. (A) Conventional and (B) AIR™ Recon DL.
Table 2.
Interobserver agreement and diagnostic accuracy evaluation. Excellent interobserver agreement for all protocols with AIR™ Recon DL were achieved.
Table 4.
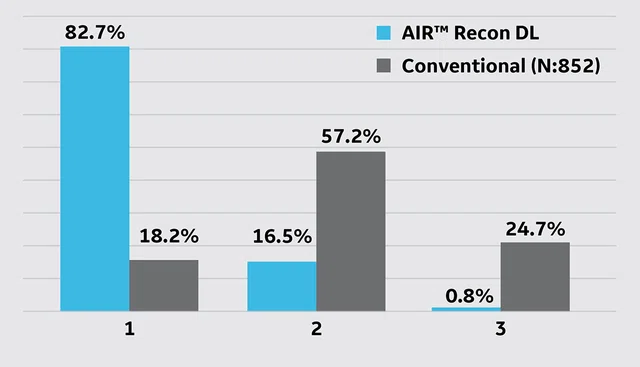
Patient perceived exam duration (1: short-very short, 2: normal, 3: long-very long).
Table 5.
Clinical workflow and productivity increase after AIR™ Recon DL implementation in two different sites: San Isidro and Pilar. Definition: Full positive band: 8 am-8 pm; Full negative band: 6-8 am and 8 pm-12 am; Positive band AIR™Recon DL system: 1-7 pm.
Table 6.
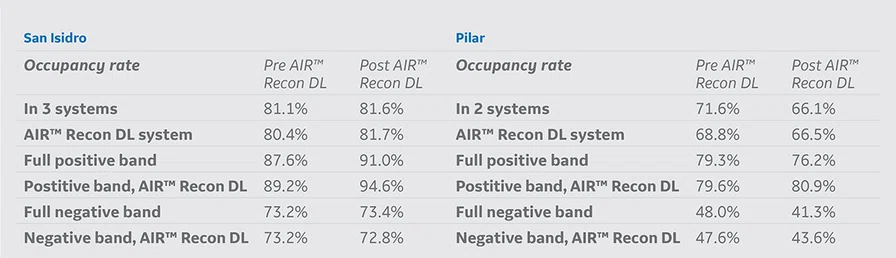
Occupancy rates before and after AIR™ Recon DL implementation.
result


PREVIOUS
${prev-page}
NEXT
${next-page}
Subscribe Now
Manage Subscription
FOLLOW US
Contact Us • Cookie Preferences • Privacy Policy • California Privacy PolicyDo Not Sell or Share My Personal Information • Terms & Conditions • Security
© 2024 GE HealthCare. GE is a trademark of General Electric Company. Used under trademark license.
IN PRACTICE
Increasing productivity while maintaining high quality of service
Increasing productivity while maintaining high quality of service
by Patricia Carrascosa, MD, PhD, FACC, FSCCT, MSCCT Diagnóstico Maipú - DASA, Buenos Aires, Argentina Institutional collaborators: Natalia Soria, MD, Carlos Capuñay, MD, and Víctor Míguez, RT
Increasing the efficiency of a clinical workflow while maintaining the high quality of a diagnostic imaging service is a worldwide challenge that must be addressed. AIR™ Recon DL, a deep-learning (DL)-based tool, is a gamechanger in this scenario. It is able to significantly improve productivity and clinical workflow while at the same time increase image quality for high diagnostic confidence and enhance the patient’s experience by reducing exam duration.
Increasing the efficiency of a clinical workflow while maintaining the high quality of a diagnostic imaging service is a worldwide challenge that must be addressed. AIR™ Recon DL, a deep-learning (DL)-based tool, is a gamechanger in this scenario. It is able to significantly improve productivity and clinical workflow while at the same time increase image quality for high diagnostic confidence and enhance the patient’s experience by reducing exam duration.
In a partnership between Diagnóstico Maipú - DASA and GE HealthCare, we have implemented AIR™ Recon DL in our routine MR imaging protocols. In this report, we demonstrate the impact of this new DL technology in our clinical routine through our imaging results and evaluation of scan times before and after the installation.
AIR™ Recon DL was implemented based on strategic decisions in several clinical routine protocols on a SIGNA™ Architect 3.0T MR system with software version DV29.1. Table 1 summarizes the protocols where it was adopted into our original conventional protocols. Exam times and schedule times, with and without AIR™ Recon DL, were extracted to analyze percent and overall average time reductions of each protocol.
AIR™ Recon DL was implemented based on strategic decisions in several clinical routine protocols on a SIGNA™ Architect 3.0T MR system with software version DV29.1. Table 1 summarizes the protocols where it was adopted into our original conventional protocols. Exam times and schedule times, with and without AIR™ Recon DL, were extracted to analyze percent and overall average time reductions of each protocol.
Clinical validation
To evaluate the diagnostic confidence of using AIR™ Recon DL, we performed an initial clinical validation. The aim was to compare the diagnostic results of the studies with and without AIR™ Recon DL in order to determine the diagnostic accuracy with the new technology.
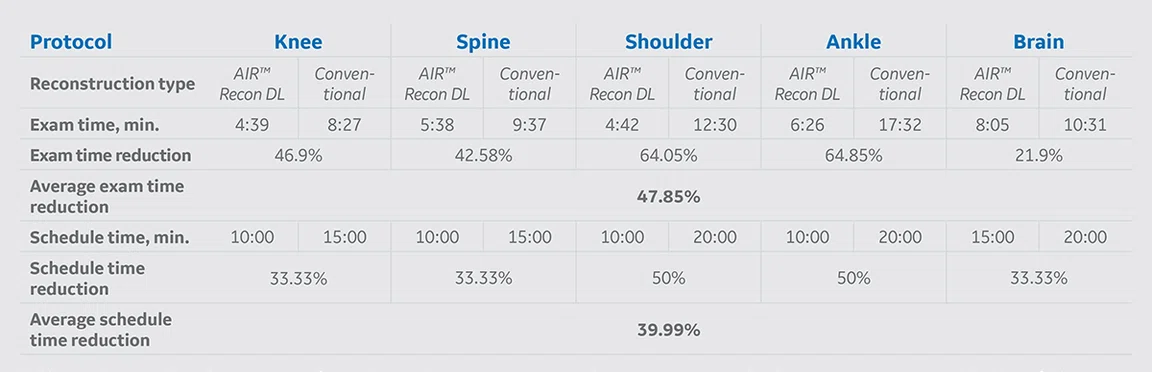
Table 1.
MR protocol implementation of AIR™ Recon DL versus conventional acquisition protocols. The average exam time reduction of all protocols where AIR™ Recon DL was applied was approximately 48% and the average schedule time reduction was nearly 40%.
Materials and methods
A group of 221 patients underwent MR exams on our SIGNA™ Architect that included both protocols with and without AIR™ Recon DL reconstruction. Two experienced observers (O1 and O2) independently analyzed each set of images, providing a diagnosis of each type of study. The results of the two observers were compared O1 (with AIR™ Recon DL) versus O2 (without AIR™ Recon DL) by calculating the interobserver agreement (kappa) and diagnostic accuracy: sensitivity (S), specificity (Sp), positive predictive value (VPP) and negative predictive value (VPN). The results are listed in Table 2. Image quality was rated through a 3-point scale (1: regular, 2: good, 3: excellent). The results are listed in Table 3.
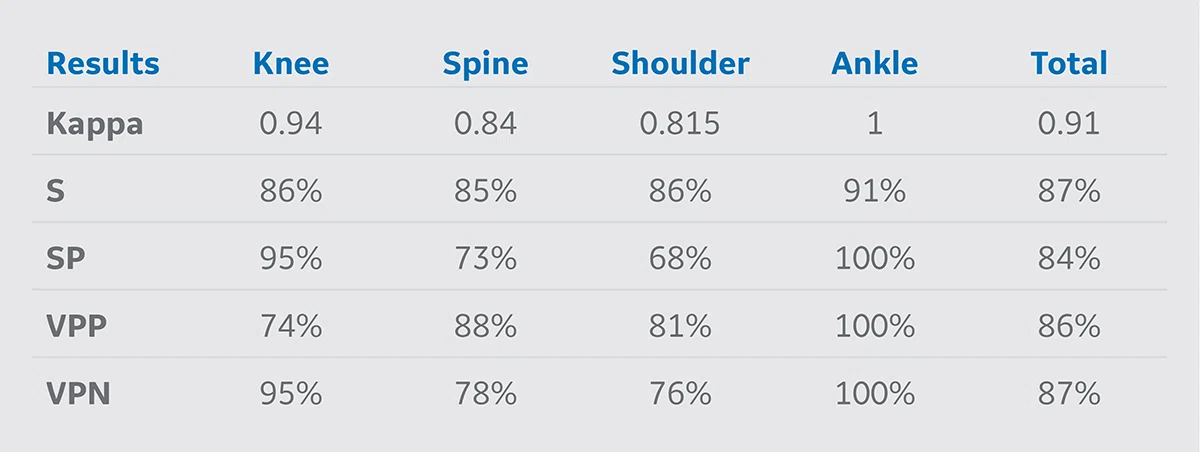
Table 2.
Interobserver agreement and diagnostic accuracy evaluation. Excellent interobserver agreement for all protocols with AIR™ Recon DL were achieved.

Table 3.
Image quality results. AIR™ Recon DL reconstructed image quality was rated higher than conventional reconstructed images (w/o AIR™ Recon DL), 2.5 and 2.3, respectively.
Patient experience
The patient experience regarding the MR exam with AIR™ Recon DL and without AIR™ Recon DL was evaluated through a survey that the patients participated in directly after their examination. The perceived duration of the examination was rated based on a 3-point scale (1: short-very short, 2: normal, 3: long-very long). The results are shown in Table 4.
Overall patient experience was evaluated by assessing the net promotor score (NPS). In a survey, the patients answered on a scale from 0-10 the probability that they would recommend the examination to friends and family. Detractors where considered 0-6, Neutral 7-8 and Promoters 9-10. NPS was calculated by: NPS = % promoters - % detractors. The NPS was 83.5.
Workflow and productivity
The impact on the clinical workflow and productivity was evaluated by measuring the number of MR exams performed before and after AIR™ Recon DL implementation for the San Isidro and Pilar sites. In the same time period, an increase of 24% and 39% were achieved in San Isidro and Pilar in a 12-hour schedule, respectively, and 14% and 31% in a full day (e.g., 19-hour schedule), respectively. The results are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Clinical workflow and productivity increase after AIR™ Recon DL implementation in two different sites: San Isidro and Pilar. Definition: Full positive band: 8 am-8 pm; Full negative band: 6-8 am and 8 pm-12 am; Positive band AIR™Recon DL system: 1-7 pm.
In Table 6, we compared the occupancy rate for the total number of systems at each site where AIR™ Recon DL is available. AIR™ Recon DL is only used in one scanner in each site. We started in a conservative way by only using AIR™ Recon DL from 1-7 pm to see if there was patient redistribution to the other scanners in the same facility. The occupancy rate was very high in the band with AIR™ Recon DL in both sites, however, in the San Isidro site it was even higher due to greater demand. The total number of patients in positive band and full-day schedules was increased using AIR™ Recon DL in both sites.
Conclusion
AIR™ Recon DL is a novel technique that reduces exam times while also maintaining or improving SNR for higher image quality and lower image noise. We found the nearly 50% reduction in exam times allowed a subsequent reduction in scheduling times of nearly 40%, significantly increasing staff productivity. Further, 82.7% of patients reported they perceived a very short exam time for their MR study. We demonstrated that AIR™ Recon DL maintains the high level of service to the patient and delivers the quality our radiologists need for confident diagnoses.
Conducting this in-house validation study allowed us to implement AIR™ Recon DL in the most efficient way for our center, with broad clinical acceptance by our staff. Measuring and quantifying the impact of this implementation enabled us to identify areas of increased productivity and plan staff resources accordingly to meet the new workflow requirements. We recommend other centers evaluate the demand and accessibility for increased MR services to develop a strategy that best fits clinical and patient needs.